每日一题 0926 路径总和 II
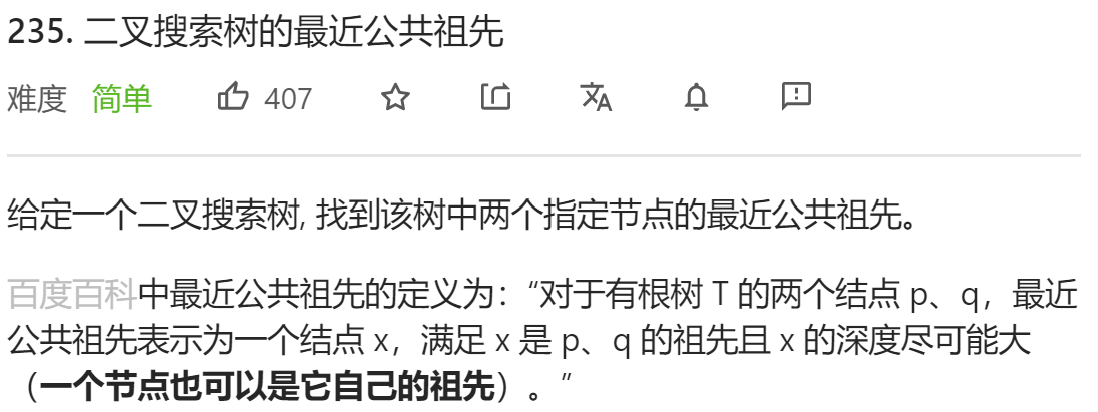
每日一题 0927 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
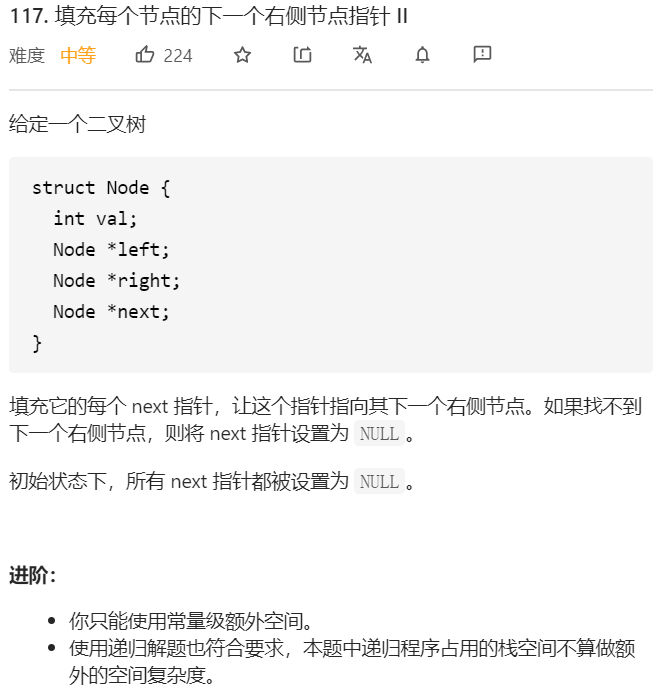
每日一题 0928 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
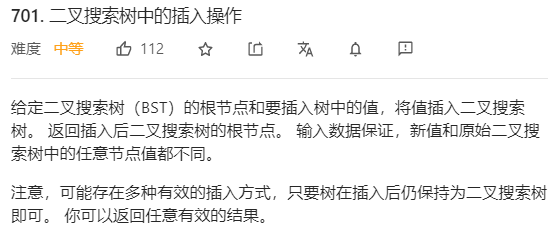
每日一题 0930 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
每日一题 1009 环形链表
每日一题 1010 环形链表II
每日一题 1011 分割等和子集
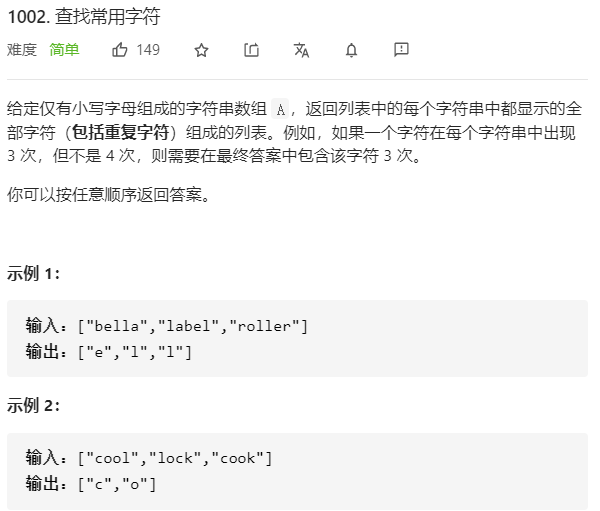
每日一题 1014 查找常用字符
每日一题 1016 有序数组的平方
每日一题 1126 最大间距
每日一题 1127 四数相加||
每日一题 1130 重构字符串
每日一题 1201 重构字符串
每日一题 1202 拼接最大数
每日一题 1203 计数质数
每日一题 1204 分割数组为连续子序列
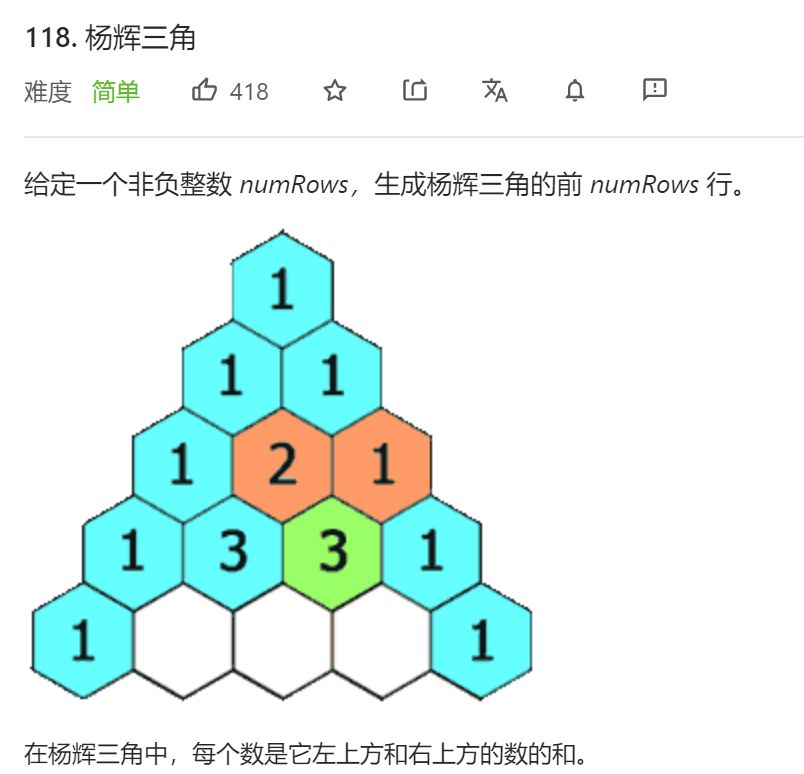
每日一题 1206 杨辉三角
每日一题 1207 杨辉三角
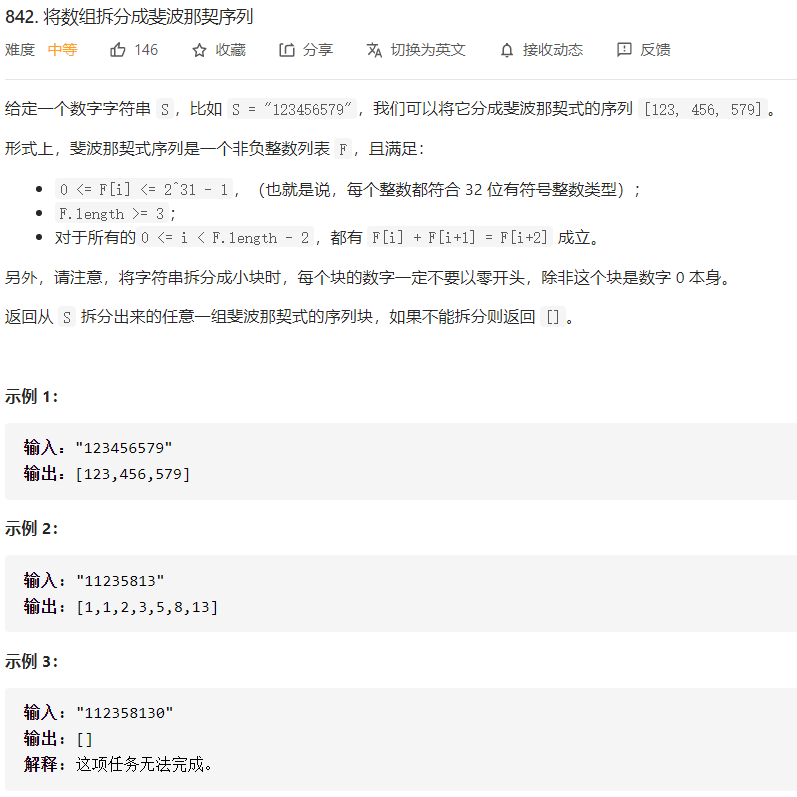
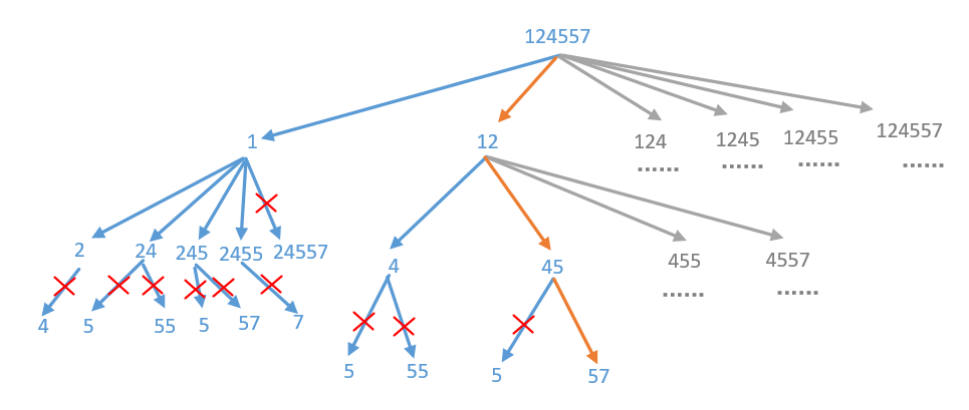
每日一题 1208 将数组拆分成斐波那契数列
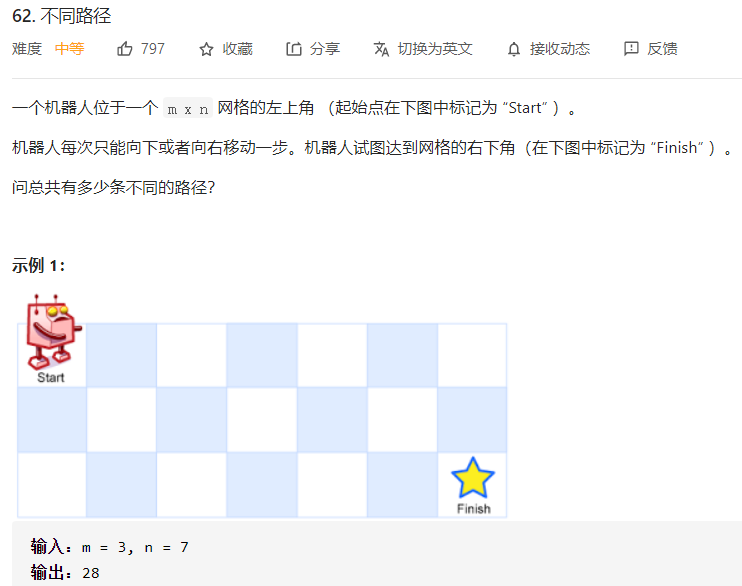
每日一题 1209 不同路径
每日一题 1210 柠檬水找零
每日一题 1211 Dota2 参议院
每日一题 1212 摆动序列
每日一题 1213 存在重复元素
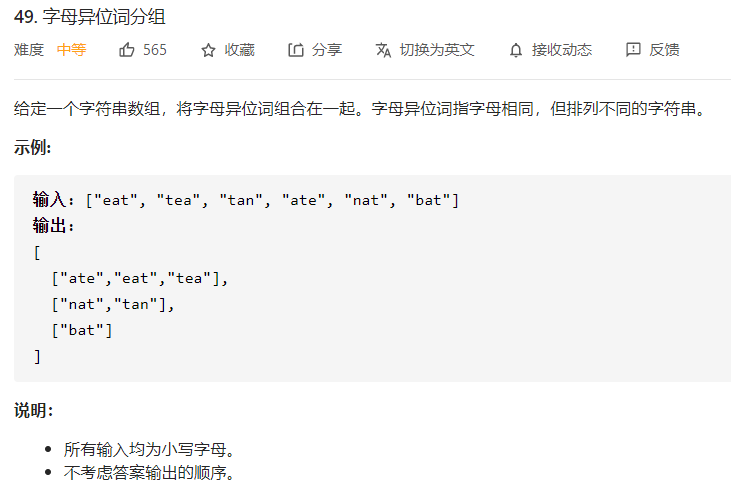
每日一题 1214 字母异位词分组
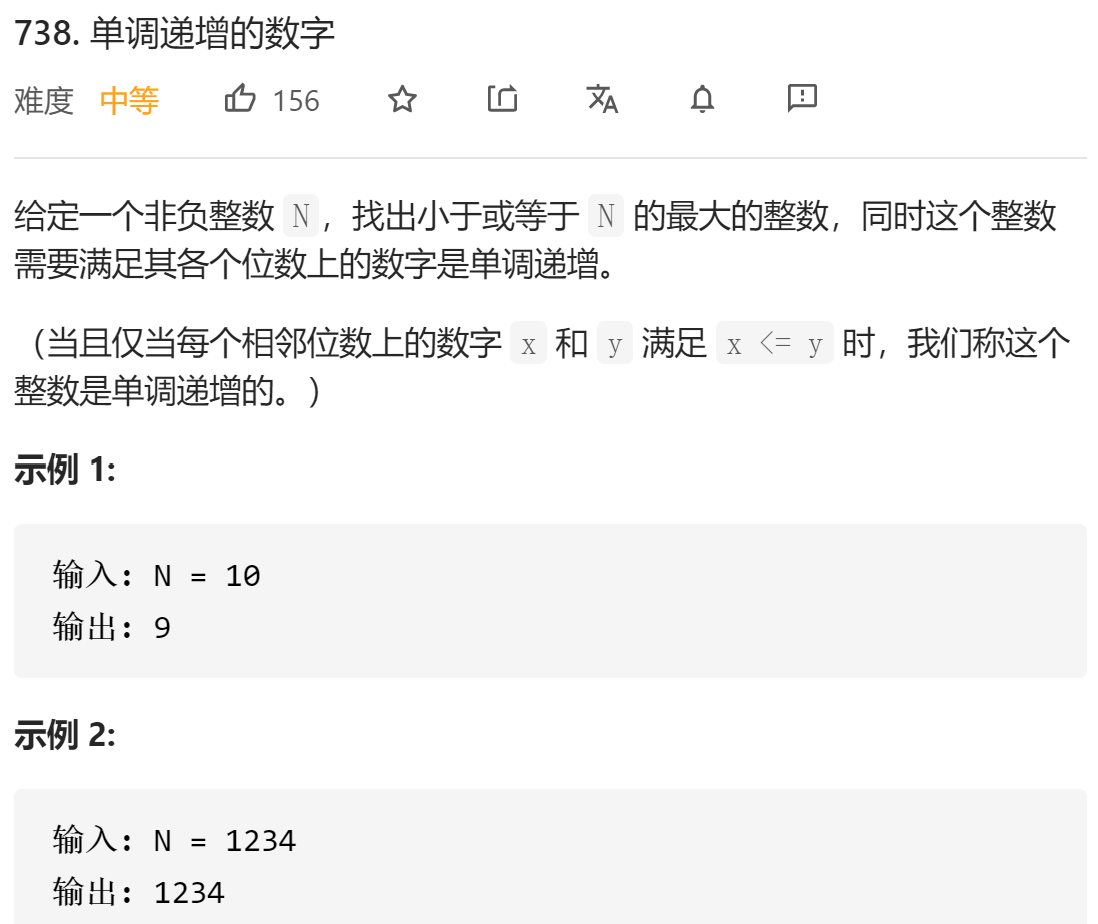
每日一题 1215 单调递增的数字
每日一题 1216 单词规律
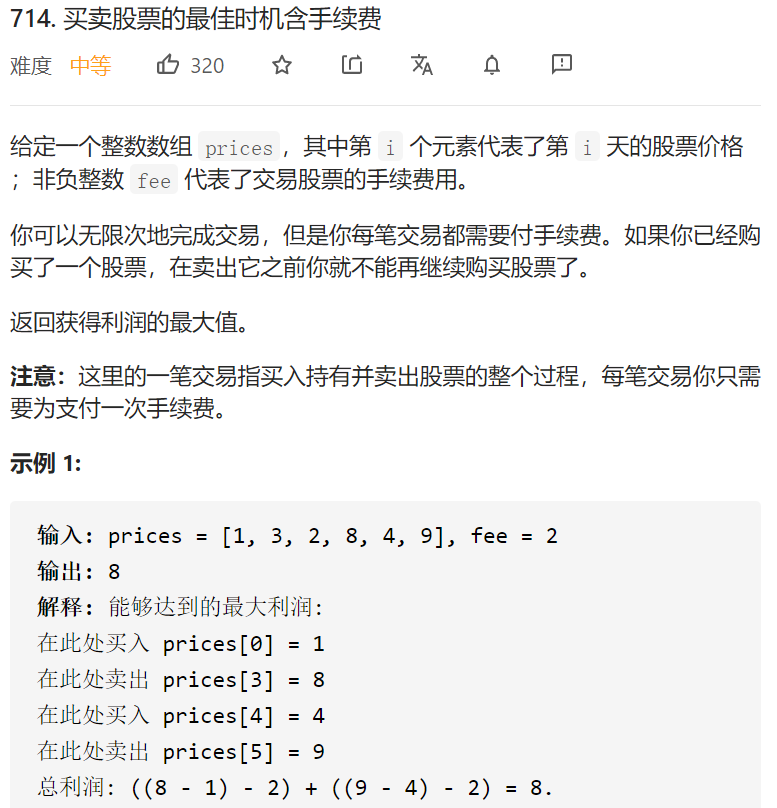
每日一题 1217 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
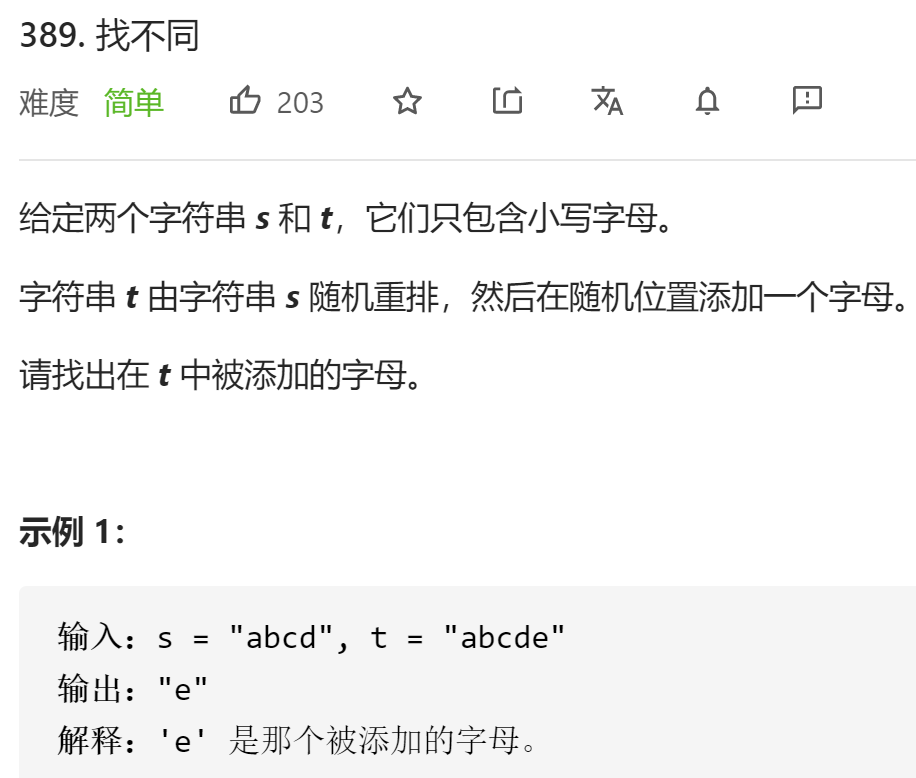
每日一题 1218 找不同
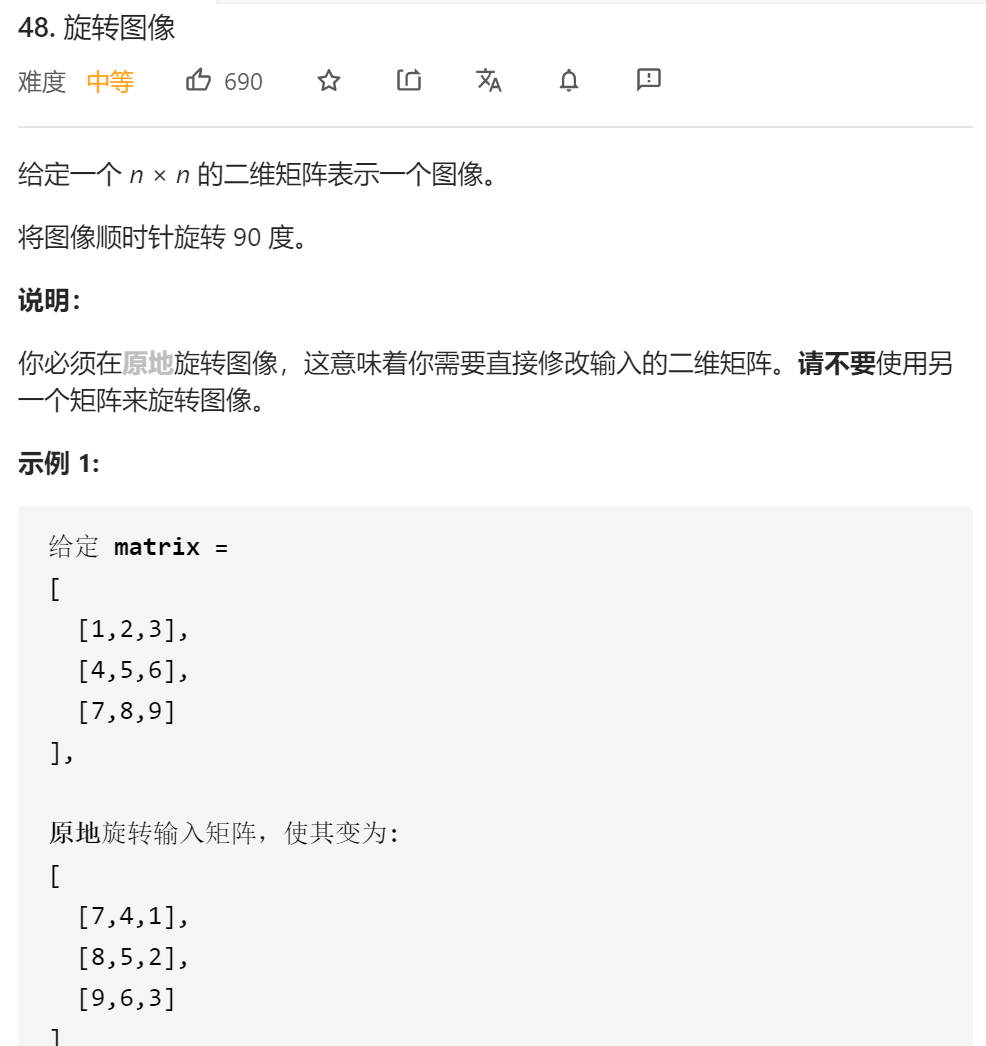
每日一题 1219 旋转图像
每日一题 1221 使用最小花费爬楼梯
每日一题 1222 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
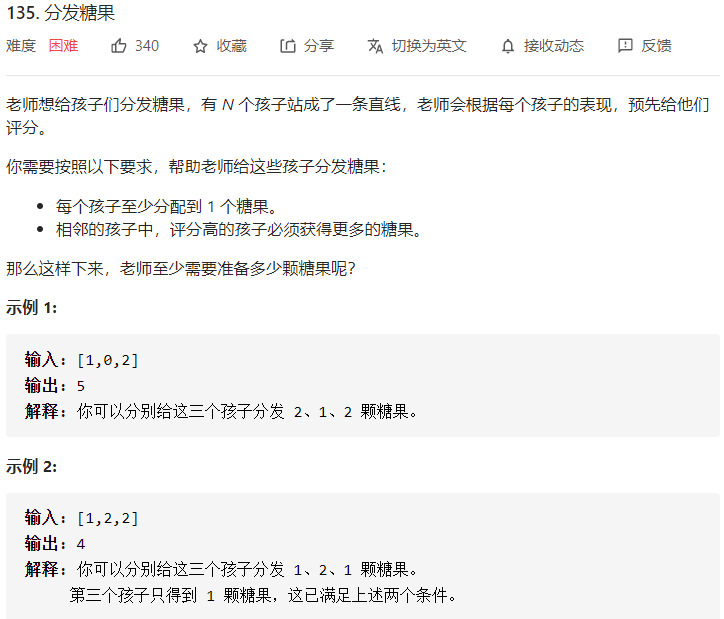
每日一题 1224 分发糖果
每日一题 1225 分发饼干
每日一题 1226 最大矩形
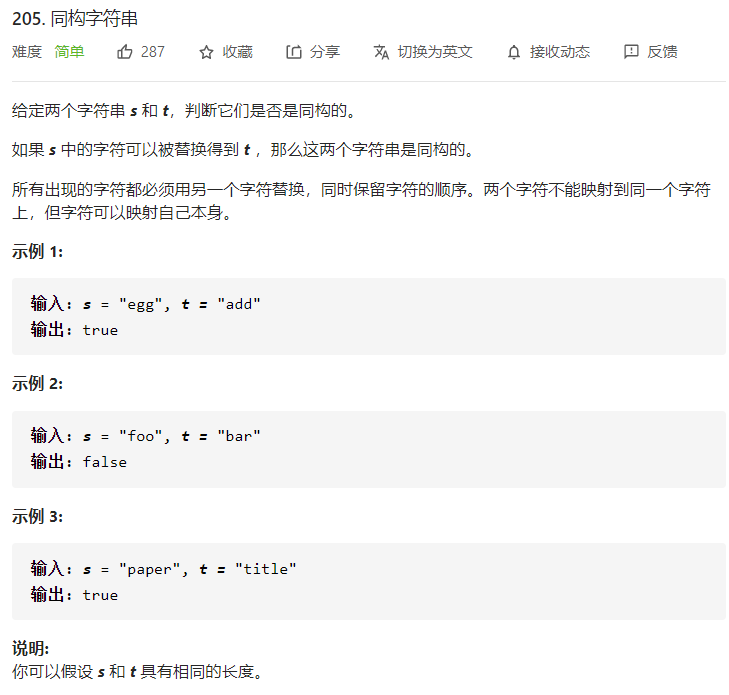
每日一题 1227 同构字符串
每日一题 1228 买卖股票的最佳时机
每日一题 1229 按要求补齐数组
每日一题 1230 最后一块石头的重量
每日一题 0102 滑动窗口最大值
每日一题 0103 分割链表
每日一题 0104 斐波那契数列
每日一题 0105 较大分组的位置
每日一题 0106 除法求值
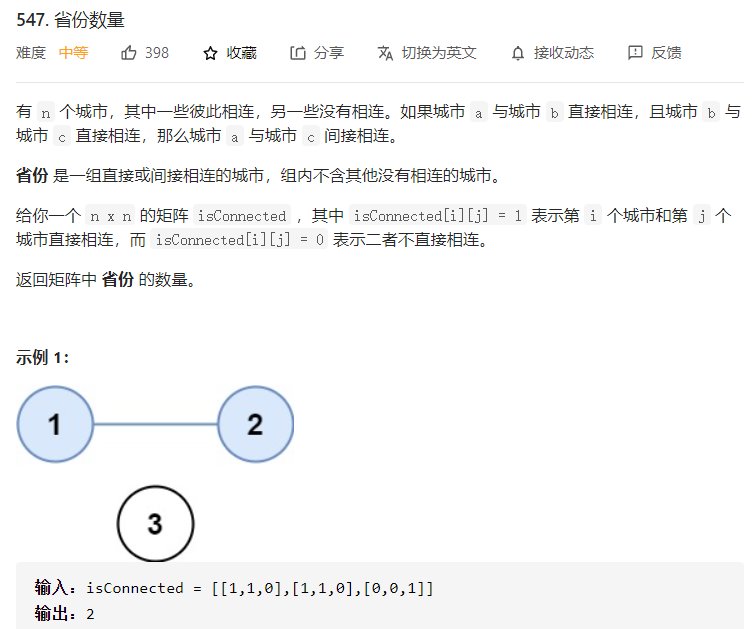
每日一题 0107 省份数量
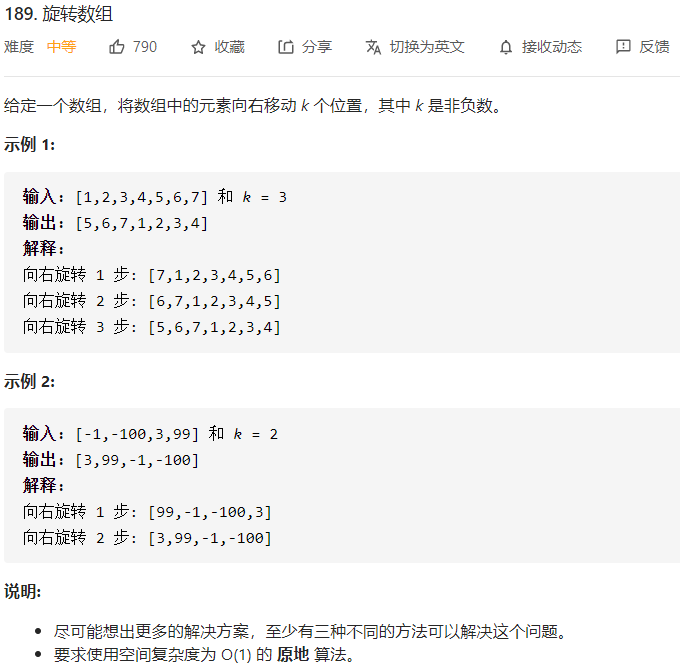
每日一题 0108 旋转数组
每日一题 0110 旋转数组
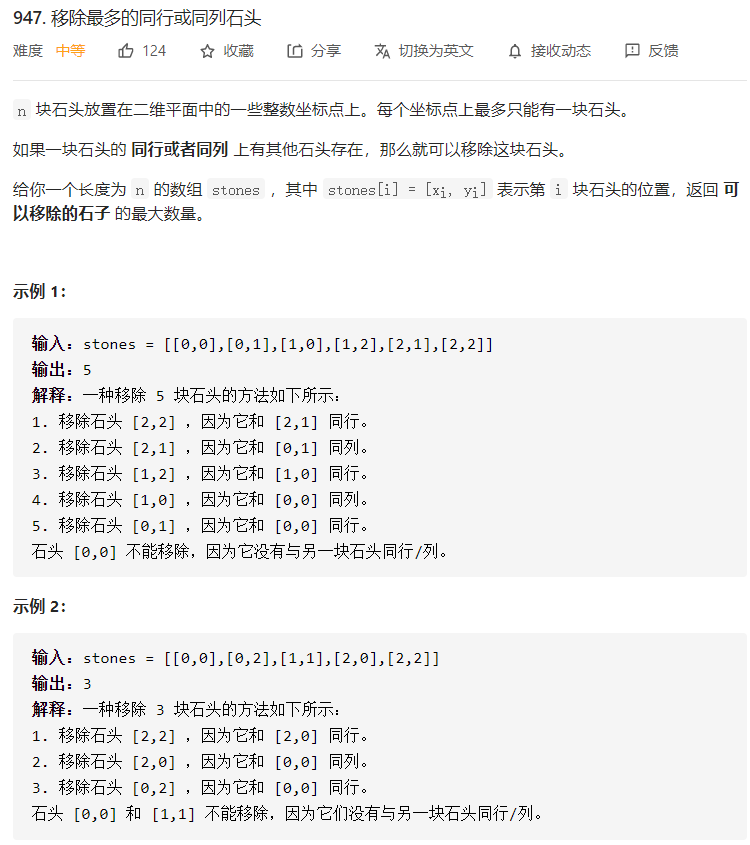
每日一题 0115 移除最多的同行或同列石头
每日一题 0122 旋转数组
每日一题 0201 公平的糖果棒交换
每日一题 0228 公平的糖果棒交换
每日一题 0301 公平的糖果棒交换
每日一题 0302 公平的糖果棒交换
每日一题 0303 比特位计数
每日一题 0304 俄罗斯套娃信封问题
每日一题 0926 二叉树中和为某一值的路径 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ''' dfs到每个叶子节点 判断路径和是否等于sum ''' class Solution (object ): def pathSum (self, root, sum ): self.path=[] self.res=[] def dfs (root,sum ): if root==None : return self.path.append(root.val) sum-=root.val if root.left==None and root.right==None and sum==0 : self.res.append(list(self.path)) dfs(root.left,sum) dfs(root.right,sum) self.path.pop() dfs(root,sum) return self.res
每日一题 0927 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 ''' 若根节点的值在两个节点中间,则根节点为最近公共祖先 若根节点大于两者的最大值,则最近公共祖先在根节点的右子树中 反之 小于最小值,在左子树中 ''' class Solution (object ): def lowestCommonAncestor (self, root, p, q ): m=p.val n=q.val if root==p or root==q: return root if root.val < min(m,n): return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q) elif root.val >max(m,n): return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q) else : return root
每日一题 0928 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 ''' 每次遍历当前层时记录下一层的节点总数 省一个栈的层序遍历 ''' class Solution (object ): def connect (self, root ): if root==None : return None stack=[root] now_count=1 next_count=0 while stack: p=stack.pop(0 ) now_count-=1 if p.left: stack.append(p.left) next_count+=1 if p.right: stack.append(p.right) next_count+=1 while now_count>0 : cur=stack.pop(0 ) p.next=cur p=cur now_count-=1 if p.left: stack.append(p.left) next_count+=1 if p.right: stack.append(p.right) next_count+=1 now_count=next_count next_count=0 return root
每日一题 0930 二叉搜索树中的插入操作 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ''' 每次遍历当前层时记录下一层的节点总数 省一个栈的层序遍历 ''' class Solution (object ): def insertIntoBST (self, root, val ): if root==None : root=TreeNode(val) else : if root.val<val: root.right=self.insertIntoBST(root.right,val) else : root.left=self.insertIntoBST(root.left,val) return root
每日一题 1009 环形链表 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 ''' 快慢指针 我们定义两个指针,一快一满。慢指针每次只移动一步,而快指针每次移动两步。 初始时,慢指针在位置 head,而快指针在位置 head.next。这样一来,如果在移动的过程中,快指针反过来追上慢指针,就说明该链表为环形链表。否则快指针将到达链表尾部,该链表不为环形链表。 ''' class Solution (object ): def hasCycle (self, head ): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: bool """ if not head or not head.next: return False slow=head fast=head.next while slow!=fast: if not fast or not fast.next: return False slow=slow.next fast=fast.next.next return True
每日一题 1010 环形链表II 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 ''' 快慢指针 分两步,第一步利用快慢指针判断是否是环形链表: 我们定义两个指针,一快一满。慢指针每次只移动一步,而快指针每次移动两步。 初始时,慢指针,快指针在位置 head,这样一来,如果在移动的过程中,快指针反过来追上慢指针,就说明该链表为环形链表。否则快指针将到达链表尾部,该链表不为环形链表。 第二步是找环形的第一个节点: 当发现 slow 与 fast 相遇时,我们再额外使用一个指针ptr。起始,它指向链表头部;随后,它和slow 每次向后移动一个位置。最终,它们会在入环点相遇。 ''' class Solution (object ): def detectCycle (self, head ): if not head or not head.next: return None slow=head fast=head while slow.next and fast.next and fast.next.next and slow.next!=fast.next.next: slow=slow.next fast=fast.next.next if slow.next==None or fast.next==None or fast.next.next==None : return None pre=head while pre!=slow.next: pre=pre.next slow=slow.next return pre
每日一题 1011 分割等和子集 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 ''' 动态规划 转化为0-1背包问题 能否在一系列配重中选择子集,使其刚好为和的一半 dp[i][j] 代表在0~i的配重中选择子集 能否使其和等于j 因为存在j=0 的情况 所以数组大小开为[len(nums)][sum+1] 分为两种情况: 1、前i-1个配重已经可以满足和的要求 即不需要第i个配重-->>dp[i-1][j] 2、需要第i个配重 则前i-1个配重只需要满足和=j-nums[i]-->>dp[i-1][j-nums[i]] ''' class Solution (object ): def canPartition (self, nums ): all_sum=0 for i in range(len(nums)): all_sum+=nums[i] if all_sum%2 ==1 : return False part_sum=all_sum//2 if max(nums)>part_sum: return False dp=[[False for col in range(part_sum+1 )] for row in range(len(nums))] for i in range(len(nums)): dp[i][0 ]=True dp[0 ][nums[0 ]]=True for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(part_sum+1 ): if dp[i][j]==True : continue if dp[i-1 ][j] or dp[i-1 ][j-nums[i]]: dp[i][j]=True return dp[len(nums)-1 ][part_sum]
每日一题 1014 查找常用字符 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 ''' 即各字符串的交集 ''' class Solution (object ): def commonChars (self, A ): c_dict=[0 ]*26 res=[] flag=1 c="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" for i in A: temp=[0 ]*26 for j in i: index=ord(j)-ord('a' ) if flag==1 : c_dict[index]+=1 else : temp[index]+=1 for index in range(len(c)): if flag==1 : break if c_dict[index]>temp[index]: c_dict[index]=temp[index] flag=0 for i in range(len(c_dict)): while c_dict[i] >0 : res.append(c[i]) c_dict[i]-=1 return res
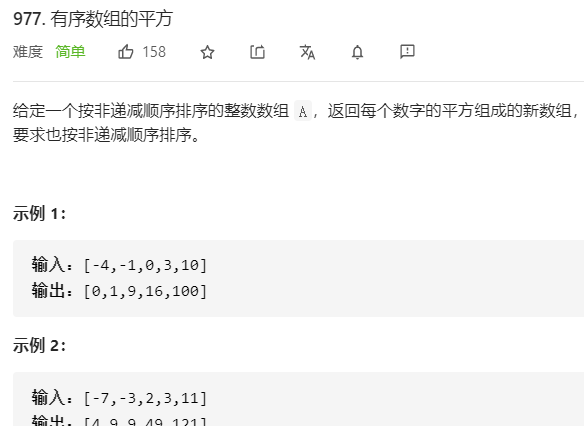
每日一题 1016 有序数组的平方 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 '' ' 双指针 最大的值一定在两侧 ' '' class Solution public int [] sortedSquares(int [] A) { int start=0 ; int end=A.length; int i=end-1 ; int [] res=new int [end--]; while (i>=0 ){ res[i--]=A[start]*A[start]>=A[end]*A[end]?A[start]*A[start++]:A[end]*A[end--]; } return res; } }
每日一题 1126 最大间距 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 '' ' 桶排序 ' '' class Solution public int maximumGap (int [] nums) int l=nums.length; if (l<2 ){ return 0 ; } int n_min=Integer.MAX_VALUE,n_max=-1 ; for (int i:nums){ if (i>n_max){ n_max=i; } if (i<n_min){ n_min=i; } } if ((n_max-n_min)==0 ){ return 0 ; } int b_size=(int )Math.ceil((double )(n_max-n_min)/(l-1 )); int b_num=l-1 ; int [] b_min=new int [b_num]; int [] b_max=new int [b_num]; Arrays.fill(b_max,-1 ); Arrays.fill(b_min,Integer.MAX_VALUE); for (int i:nums){ if (i==n_max || i==n_min) continue ; int index=(i-n_min)/b_size; b_max[index]=Math.max(b_max[index],i); b_min[index]=Math.min(b_min[index],i); } int res=0 ; int premax=n_min; for (int i=0 ;i<b_num;i++){ if (b_max[i]==-1 ) continue ; res=Math.max(b_min[i]-premax,res); premax=b_max[i]; } res=Math.max(n_max-premax,res); return res; } } class Solution public int maximumGap (int [] nums) int n = nums.length; if (n < 2 ) { return 0 ; } int minVal = Arrays.stream(nums).min().getAsInt(); int maxVal = Arrays.stream(nums).max().getAsInt(); int d = Math.max(1 , (maxVal - minVal) / (n - 1 )); int bucketSize = (maxVal - minVal) / d + 1 ; int [][] bucket = new int [bucketSize][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < bucketSize; ++i) { Arrays.fill(bucket[i], -1 ); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int idx = (nums[i] - minVal) / d; if (bucket[idx][0 ] == -1 ) { bucket[idx][0 ] = bucket[idx][1 ] = nums[i]; } else { bucket[idx][0 ] = Math.min(bucket[idx][0 ], nums[i]); bucket[idx][1 ] = Math.max(bucket[idx][1 ], nums[i]); } } int ret = 0 ; int prev = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < bucketSize; i++) { if (bucket[i][0 ] == -1 ) { continue ; } if (prev != -1 ) { ret = Math.max(ret, bucket[i][0 ] - bucket[prev][1 ]); } prev = i; } return ret; } }
每日一题 1127 四数相加|| 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 '' ' 遍历 A 和 B 所有元素和的组合情况,并记录在 ab_map 中,ab_map 的 key 为两数和,value 为该两数和出现的次数 遍历 C 和 D 所有元素和的组合情况,取和的负值判断其是否在 ab_map 中,若存在则取出 ab_map 对应的 value 值,count = count + value ' '' class Solution public int fourSumCount (int [] A, int [] B, int [] C, int [] D) Map<Integer, Integer> countAB = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for (int u : A) { for (int v : B) { countAB.put(u + v, countAB.getOrDefault(u + v, 0 ) + 1 ); } } int ans = 0 ; for (int u : C) { for (int v : D) { if (countAB.containsKey(-u - v)) { ans += countAB.get(-u - v); } } } return ans; } }
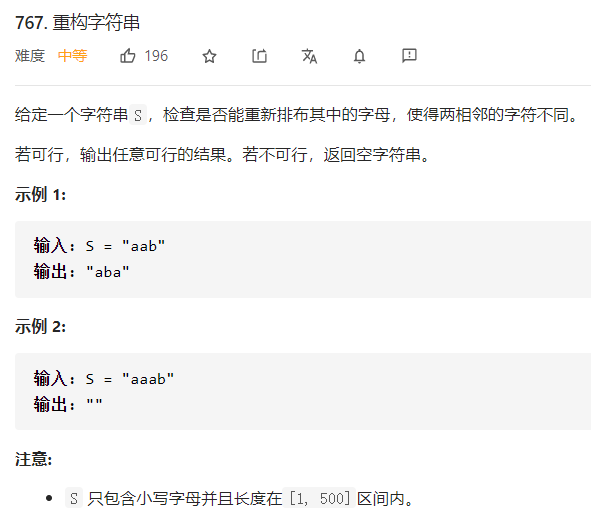
每日一题 1130 重构字符串 一、问题描述
问题思路
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 '' ' 遍历 A 和 B 所有元素和的组合情况,并记录在 ab_map 中,ab_map 的 key 为两数和,value 为该两数和出现的次数 遍历 C 和 D 所有元素和的组合情况,取和的负值判断其是否在 ab_map 中,若存在则取出 ab_map 对应的 value 值,count = count + value ' '' class Solution public String reorganizeString (String S) int all_l=S.length(); if (all_l<2 ){ return S; } int [] charnum=new int [26 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<all_l;i++){ char ch=S.charAt(i); charnum[(int )(ch-'a' )]++; if (charnum[(int )(ch-'a' )]>(all_l+1 )/2 ){ return "" ; } } PriorityQueue<Character> queue=new PriorityQueue<Character>(new Comparator<Character>() { @Override public int compare (Character o1, Character o2) return charnum[(int )(o2-'a' )]-charnum[(int )(o1-'a' )]; } }); for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++){ if (charnum[i]>0 ){ queue.offer((char )(i+97 )); } } StringBuilder res=new StringBuilder(); while (queue.size()>1 ){ char q1=queue.poll(); char q2=queue.poll(); res.append(q1); res.append(q2); if (--charnum[q1-'a' ]>0 ){ queue.offer(q1); } if (--charnum[q2-'a' ]>0 ){ queue.offer(q2); } } if (queue.size()>0 ){ res.append(queue.poll()); } return res.toString(); } }
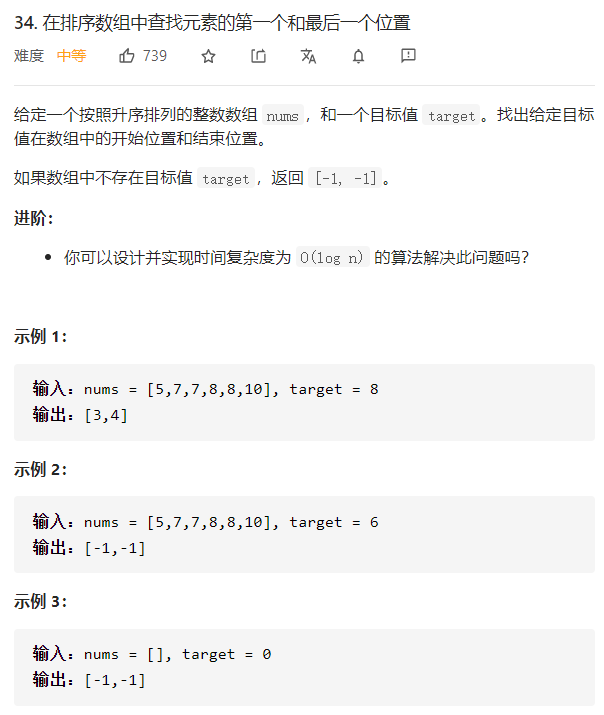
每日一题 1201 重构字符串 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 '' ' 二分查找找到该数后 向两边拓展找到全部数字 ' '' class Solution public int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { int low=0 ; int high=nums.length-1 ; int pivot=(low+high)/2 ; int [] res={-1 ,-1 }; if (nums.length==0 ){ return res; } while (nums[pivot]!=target){ if (nums[pivot]>target){ high=pivot-1 ; } else { low=pivot+1 ; } if (high<low){ return res; } pivot=(low+high)/2 ; } low=pivot-1 ; high=pivot+1 ; while (low>=0 && nums[low]==target)low--; while (high<nums.length&&nums[high]==target)high++; res[0 ]=low+1 ; res[1 ]=high-1 ; return res; } }
每日一题 1202 拼接最大数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 "" " 为了找到长度为 k 的最大数,需要从两个数组中分别选出最大的子序列,这两个子序列的长度之和为 k,然后将这两个子序列合并得到最大数。两个子序列的长度最小为 0,最大不能超过 kk 且不能超过对应的数组长度。 " "" class Solution public int [] maxNumber(int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int k) { int l1=nums1.length; int l2=nums2.length; int start=Math.max(0 ,k-l2); int end=Math.min(k,l1); int [] maxres=new int [k]; for (int i=start;i<=end;i++){ int [] sub1=maxSub(nums1,i); int [] sub2=maxSub(nums2,k-i); int [] tempmax=merge(sub1,sub2); if (compare(tempmax,0 ,maxres,0 )>0 ){ System.arraycopy(tempmax,0 ,maxres,0 ,k); } } return maxres; } public int [] maxSub(int [] nums,int k ){ int [] stack=new int [k]; int top=-1 ; int remain=nums.length-k; for (int i=0 ;i<nums.length;i++){ int num=nums[i]; while ( top>=0 && stack[top]<num && remain>0 ){ top--; remain--; } if (top<k-1 ){ stack[++top]=num; } else { remain--; } } return stack; } public int [] merge(int [] sub1,int [] sub2){ int l1=sub1.length; int l2=sub2.length; int [] res=new int [l1+l2]; if (l1==0 ){ return sub2; } if (l2==0 ){ return sub1; } int i=0 ; int index1=0 ; int index2=0 ; while (index1<l1||index2<l2){ if (compare(sub1,index1,sub2,index2)>0 ){ res[i]=sub1[index1++]; } else { res[i]=sub2[index2++]; } i++; } return res; } public int compare (int [] sub1,int index1,int [] sub2,int index2) while (index1<sub1.length&&index2<sub2.length){ if (sub1[index1]!=sub2[index2]){ return sub1[index1]-sub2[index2]; } index1++; index2++; } return (sub1.length-index1)-(sub2.length-index2); } }
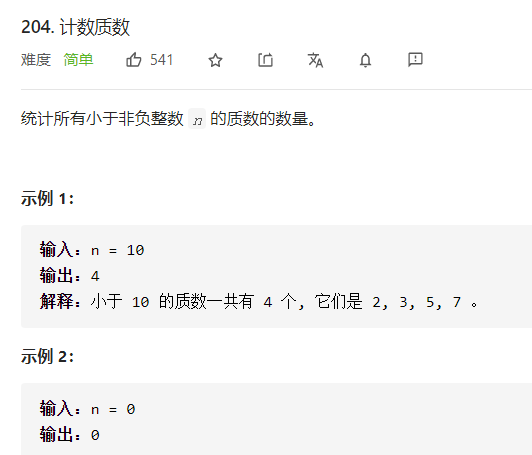
每日一题 1203 计数质数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 "" " 方法一:枚举 判断每一个数是否为质数 判断方法是看[2,根号x]是否为其因数 " "" class Solution public int countPrimes (int n) int res=0 ; for (int i=2 ;i<n;i++){ res+=isPrime(i)?1 :0 ; } return res; } public boolean isPrime (int num) for (int i=2 ;i*i<=num;i++){ if (num%i==0 ){ return false ; } } return true ; } } "" " 方法二:埃氏筛 若一个数为质数 则其倍数都为合数 从x*x开始赋为合数 因为其余的2x 3x都会在x之前就被其他数的倍数标记过了,例如2 的所有倍数,3 的所有倍数等。 " "" class Solution public static int countPrimes (int n) int res=0 ; int [] prime=new int [n]; Arrays.fill(prime,1 ); for (int i=2 ;i<n;i++){ if (prime[i]==1 ){ res+=1 ; if ((long )i*i<n){ for (int x=i*i;x<n;x+=i){ prime[x]=0 ; } } } } return res; } }
每日一题 1204 分割数组为连续子序列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 "" " 贪心 对于数组中的元素 x,如果存在一个子序列以x−1 结尾,则可以将 x加入该子序列中。将 x 加入已有的子序列总是比新建一个只包含 x 的子序列更优,因为前者可以将一个已有的子序列的长度增加 1,而后者新建一个长度为 1 的子序列,而题目要求分割成的子序列的长度都不小于 3,因此应该尽量避免新建短的子序列。 " "" public static boolean isPossible (int [] nums) HashMap<Integer,Integer> numscntmap=new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); HashMap<Integer,Integer> numsendmap=new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); for (int num:nums){ numscntmap.put(num,numscntmap.getOrDefault(num,0 )+1 ); } for (int num:nums){ if (numscntmap.get(num)==0 ) { continue ; } numscntmap.put(num,numscntmap.get(num)-1 ); if (numsendmap.containsKey(num-1 )&& numsendmap.get(num-1 )>0 ){ numsendmap.put(num-1 ,numsendmap.get(num-1 )-1 ); numsendmap.put(num,numsendmap.getOrDefault(num,0 )+1 ); } else if (numscntmap.containsKey(num+1 )&&numscntmap.get(num+1 )>0 &&numscntmap.containsKey(num+2 )&&numscntmap.get(num+2 )>0 ){ numsendmap.put(num+2 ,numsendmap.getOrDefault(num+2 ,0 )+1 ); numscntmap.put(num+1 ,numscntmap.get(num+1 )-1 ); numscntmap.put(num+2 ,numscntmap.get(num+2 )-1 ); } else { return false ; } } return true ; }
每日一题 1206 杨辉三角 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 主要是二维集合的初始化和赋值 杨辉三角就是第i层的元素个数都为i 第i层第j个元素的值等于 第i-1层第j-1个元素+第i-1层第j个元素 注意j的范围[1,i-1] " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < numRows; i++) { ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); temp.add(1 ); for (int j = 1 ; j < i; j++) { int sumnum = res.get(i - 1 ).get(j - 1 ) + res.get(i - 1 ).get(j); temp.add(sumnum); } if (i > 0 ) { temp.add(1 ); } res.add(temp); } return (List)res; } }
每日一题 1207 杨辉三角 一、问题描述
二、具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 贪心 理清逻辑思路 不需要实际去改变矩阵 " "" class Solution public int matrixScore (int [][] A) int m=A.length; int n=A[0 ].length; int res=m*(1 <<(n-1 )); for (int i=1 ;i<n;i++){ int temp_num=0 ; for (int j=0 ;j<m;j++){ if (A[j][0 ]==0 ){ temp_num+=1 -A[j][i]; } else { temp_num+=A[j][i]; } } temp_num=Math.max(temp_num,m-temp_num); res+=temp_num*(1 <<(n-1 -i)); } return res; } }
每日一题 1208 将数组拆分成斐波那契数列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 "" " 回溯 " "" public List<Integer> splitIntoFibonacci (String S) List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); backtrack(S.toCharArray(), res, 0 ); return res; } public boolean backtrack (char [] digit, List<Integer> res, int index) if (index == digit.length && res.size() >= 3 ) { return true ; } for (int i = index; i < digit.length; i++) { if (digit[index] == '0' && i > index) { break ; } long num = subDigit(digit, index, i + 1 ); if (num > Integer.MAX_VALUE) { break ; } int size = res.size(); if (size >= 2 && num > res.get(size - 1 ) + res.get(size - 2 )) { break ; } if (size <= 1 || num == res.get(size - 1 ) + res.get(size - 2 )) { res.add((int ) num); if (backtrack(digit, res, i + 1 )) return true ; res.remove(res.size() - 1 ); } } return false ; } private long subDigit (char [] digit, int start, int end) long res = 0 ; for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { res = res * 10 + digit[i] - '0' ; } return res; }
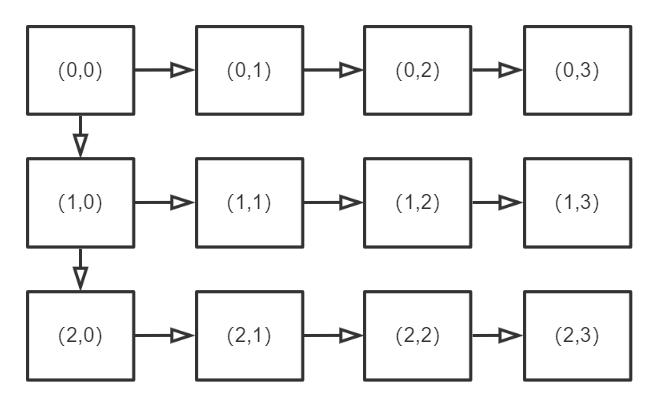
每日一题 1209 不同路径 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 动态规划 只能通过左边或者上面到达当前节点:dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-1]+dp[i-1][j]; " "" class Solution public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) int [][] dp=new int [m][n]; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ dp[i][0 ]=1 ; } for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ dp[0 ][i]=1 ; } for (int i=1 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<n;j++){ dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-1 ]+dp[i-1 ][j]; } } return dp[m-1 ][n-1 ]; } }
每日一题 1210 柠檬水找零 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 "" " 用两个int变量存老板手上5元和10元张数 " "" class Solution public boolean lemonadeChange (int [] bills) int five=0 ; int ten=0 ; for (int bill:bills){ if (bill==5 ){ five+=1 ; } else if (bill==10 ){ if (five<0 ) return false ; else { five-=1 ; ten+=1 ; } } else { if (ten>0 &&five>0 ){ ten-=1 ; five-=1 ; } else if (five>=3 ){ five-=3 ; } else { return false ; } } } return true ; } }
每日一题 1211 Dota2 参议院 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 "" " 贪心算法:每个R阵营的参议员禁止下一个离他最近的D阵营的参议员,反之亦然。 * 算法流程: * 使用两个队列分别保存R阵营和D阵营的参议员索引, * 在每一轮循环中,比较相邻两个R和D阵营的参议员的索引, * 保留索引小(min)的,并将该(min + senate.length)添加到该阵营队列尾部 * 去除索引大的,即不添加到末尾。 " "" class Solution public String predictPartyVictory (String senate) Queue<Integer> r=new LinkedList<Integer>(); Queue<Integer> d=new LinkedList<Integer>(); for (int i=0 ;i<senate.length();i++){ if (senate.charAt(i)=='R' ){ r.offer(i); } else { d.offer(i); } } while (!r.isEmpty()&&!d.isEmpty()){ int r_idx=r.remove(); int d_idx=d.remove(); if (r_idx<d_idx) r.add(r_idx+senate.length()); else d.add(d_idx+senate.length()); } return r.isEmpty()?"Dire" :"Radiant" ; } }
每日一题 1212 摆动序列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 "" " 动态规划 谷:nums[i]<nums[i-1] 峰:nums[i]>nums[i-1] 若是谷: 1、上一个峰+1(把i纳入序列) 2、上一个谷(不纳入序列) 选择12中大的更新谷 峰相反即可。 " "" class Solution public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) int down=1 ,up=1 ; if (nums.length<2 ){ return nums.length; } for (int i=1 ;i<nums.length;i++){ if (nums[i]<nums[i-1 ]){ down=Math.max(down,up+1 ); } else if (nums[i]>nums[i-1 ]){ up=Math.max(down+1 ,up); } } return Math.max(up,down); } }
每日一题 1213 存在重复元素 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution public boolean containsDuplicate (int [] nums) Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); for (int x : nums) { if (!set.add(x)) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
每日一题 1214 字母异位词分组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 "" " 排序 " "" class Solution public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) { List <List<String>> res= new ArrayList<>(); int idx=0 ; Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); for (int i=0 ;i<strs.length;i++){ String temp=sortstring(strs[i]); if (map.containsKey(temp)){ List<String> strtemp=new ArrayList<>(); strtemp=res.get(map.get(temp)); strtemp.add(strs[i]); res.set(map.get(temp),strtemp); } else { map.put(temp,idx); List<String> res_temp=new ArrayList<>(); res_temp.add(strs[i]); res.add(res_temp); idx+=1 ; } } return res; } public String sortstring (String s) char [] temp=s.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(temp); return s.valueOf(temp); } } "" " 大神简易写法 直接用map 存字母异位词 以及对应的字符串list 最后再把map转二维list " "" class Solution public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) { Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); for (String str : strs) { char [] array = str.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(array); String key = new String(array); List<String> list = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<String>()); list.add(str); map.put(key, list); } return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values()); } }
每日一题 1215 单调递增的数字 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 "" " 使用贪心法 若原本单调递增则直接返回 如果前面的值大于后面的值就把当前位数减一然后把后面的值变成9 " "" "" " 我自己写的 很多可以直接用内置函数完成 " "" public int monotoneIncreasingDigits (int N) if (N<10 ){ return N; } int [] ori=new int [10 ]; int [] res=new int [10 ]; int idx=0 ; while (N>0 ){ ori[idx]=N%10 ; N=N/10 ; idx+=1 ; } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ori)); int len=idx; idx-=1 ; for (int i=idx;i>=0 ;i--){ if (i>0 &&ori[i]>ori[i-1 ]){ while (i<len&&ori[i]-1 <ori[i+1 ]){ i+=1 ; } res[i]=ori[i]-1 ; i-=1 ; while (i>=0 ){ res[i]=9 ; i-=1 ; } break ; } else { res[i]=ori[i]; } } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(res)); int result=0 ; for (int i=len-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ result=result*10 ; result+=res[i]; } return result; } "" " 大神简易版 " "" public int monotoneIncreasingDigits (int N) char [] ori=String.valueOf(N).toCharArray(); int len=ori.length; for (int i=len-1 ;i>0 ;i--){ if (ori[i]<ori[i-1 ]){ ori[i-1 ]-=1 ; for (int j=i;j<len;j++){ ori[j]='9' ; } } } return Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(ori)); }
每日一题 1216 单词规律 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution public boolean wordPattern (String pattern, String s) String[] s1=s.split(" " ); char [] p1=pattern.toCharArray(); if (s1.length!=p1.length){ return false ; } Map<Character,String> map=new HashMap<>(); for (int i=0 ;i<p1.length;i++){ for (char key:map.keySet()){ String value=map.get(key); } if (map.containsKey(p1[i])){ if (map.get(p1[i]).equals(s1[i])){ continue ; } else return false ; } else { if (map.containsValue(s1[i])){ return false ; } else map.put(p1[i],s1[i]); } } return true ; } }
每日一题 1217 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 "" " 动态规划 第i天手上没有股票的最大利润=max(第i-1天没有股票的最大利润,第i-1天有股票的最大利润+第i天买了股票赚的钱(股票价格-手续费) 第i天手上有股票的最大利润=max(第i-1天有股票的最大利润,第i-1天没有股票的最大利润-第i天买股票的钱(股票价格) " "" class Solution public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) int have=-prices[0 ]; int nohave=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<prices.length;i++){ int temp=have; have=Math.max(have,nohave-prices[i]); nohave=Math.max(nohave,temp+prices[i]-fee); } return nohave; } }
每日一题 1218 找不同 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 "" " 1、求和 求字符串各个字符的和 两个和之差就是答案 " "" class Solution public char findTheDifference (String s, String t) int sums=0 ,sumt=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.length();i++){ sums+=s.charAt(i); sumt+=t.charAt(i); } sumt+=t.charAt(s.length()); return (char )(sumt-sums); } } "" " 2、位运算 将字符串拼接起来 用位运算 就成了找出现字符次数为奇数的字符问题了 异或就可以 " "" class Solution public char findTheDifference (String s, String t) int res=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.length();i++){ res=res^(int )s.charAt(i); } for (int i=0 ;i<t.length();i++){ res=res^(int )t.charAt(i); } return (char )res; } }
每日一题 1219 旋转图像 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 顺时针选择90度=先水平翻转 再主对角线翻转 " "" class Solution public void rotate (int [][] matrix) int len=matrix.length; for (int i=0 ;i<len/2 ;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<len;j++){ int temp=matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j]=matrix[len-i-1 ][j]; matrix[len-i-1 ][j]=temp; } } for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ for (int j=len-1 ;j>i;j--){ int temp=matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i]=temp; } } } }
每日一题 1221 使用最小花费爬楼梯 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 动态规划 dp2=Math.min(dp1+cost[idx-2],dp2+cost[idx-1]);//取从下两级迈步和下一级迈步中的最小值 dp代表到达第几级所需的体力 还没有迈步 cost代表从第几级迈步所需的体力 (题目描述有点问题 记得动态规划就可以) " "" class Solution public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) int dp1=0 ,dp2=0 ; int idx=2 ; while (idx<=cost.length){ int temp=dp2; dp2=Math.min(dp1+cost[idx-2 ],dp2+cost[idx-1 ]); dp1=temp; idx+=1 ; } return dp2; } }
每日一题 1222 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 "" " 二叉树的单栈层序遍历 由于知道每层的个数 直接在遍历本层的时候 赋值list 用boolean变量标记头入还是尾入 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> res=new LinkedList<>(); Queue<TreeNode> nowstack=new LinkedList<>(); if (root!=null ) nowstack.offer(root); Boolean flag=true ; while (!nowstack.isEmpty()){ Deque<Integer> temp=new LinkedList<>(); int len=nowstack.size(); while (len>0 ){ TreeNode p=nowstack.poll(); if (flag)temp.offerLast(p.val); else temp.offerFirst(p.val); if (p.left!=null ){ nowstack.offer(p.left); } if (p.right!=null ){ nowstack.offer(p.right); } len--; } flag=!flag; res.add(new LinkedList<Integer> (temp)); } return res; } }
每日一题 1224 分发糖果 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 "" " 波谷必为1 至于波峰要看左右两个波谷递增上来 取其最大值 " "" class Solution public int candy (int [] ratings) int res=0 ; int len=ratings.length; int [] left=new int [len]; left[0 ]=1 ; int [] right=new int [len]; right[len-1 ]=1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<len;i++){ if (ratings[i]>ratings[i-1 ]) left[i]=left[i-1 ]+1 ; else left[i]=1 ; } for (int i=len-1 ;i>0 ;i--){ if (ratings[i-1 ]>ratings[i]) right[i-1 ]=right[i]+1 ; else right[i-1 ]=1 ; } for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ res+=Math.max(right[i],left[i]); } return res; } }
每日一题 1225 分发饼干 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 排序+贪心 每次将最小满足该孩子的饼干 分给孩子 " "" class Solution public int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) Arrays.sort(g); Arrays.sort(s); int i=0 ,j=0 ; int count=0 ; while (i<g.length&&j<s.length){ while (j<s.length&&g[i]>s[j]) j++; if (j==s.length) break ; count+=1 ; i++; j++; } return count; } }
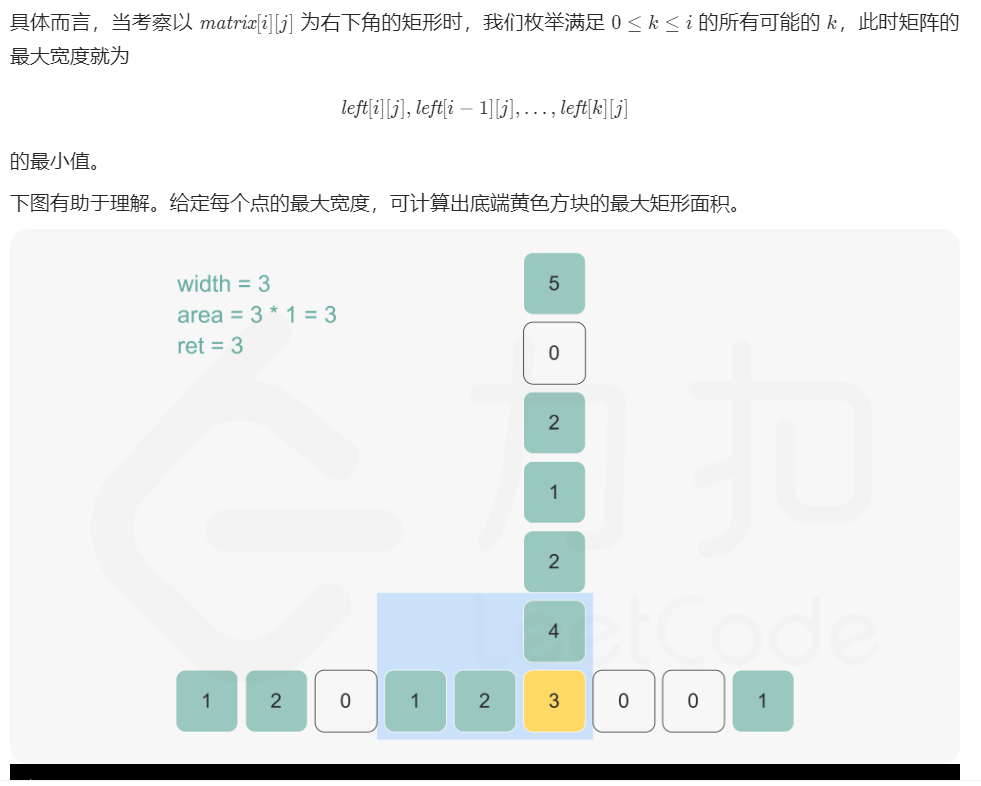
每日一题 1226 最大矩形 一、问题描述
二、具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 "" " 暴力 left[i][j]记录节点ij左边的1的个数(包括本身 " "" class Solution public int maximalRectangle (char [][] matrix) if (matrix.length==0 ||matrix[0 ].length==0 ) return 0 ; int m=matrix.length,n=matrix[0 ].length; int [][] left = new int [m][n]; int width=0 ,area=0 ,res=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ if (matrix[i][j]=='0' ){ continue ; } else { left[i][j]=(j==0 ?0 :left[i][j-1 ])+1 ; } } } for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++) { if (matrix[i][j]=='0' ) continue ; width=left[i][j]; area=width; for (int k=i-1 ;k>=0 ;k--){ width=Math.min(width,left[k][j]); area=Math.max(area,width*(i-k+1 )); } res=Math.max(res,area); } } return res; } } "" " 2、单调栈 " "" class Solution public int maximalRectangle (char [][] matrix) if (matrix.length==0 ||matrix[0 ].length==0 ) return 0 ; int m=matrix.length,n=matrix[0 ].length; int [][] left = new int [m][n]; int width=0 ,area=0 ,res=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ if (matrix[i][j]=='0' ){ continue ; } else { left[i][j]=(j==0 ?0 :left[i][j-1 ])+1 ; } } } Deque<Integer> stack=new ArrayDeque<>(); int [] tmp=new int [m+2 ]; for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ tmp[i+1 ]=left[i][j]; } for (int i=0 ;i<m+2 ;i++){ while (!stack.isEmpty()&&tmp[i]<tmp[stack.peek()]){ int h=tmp[stack.pop()]; area=Math.max(area,(i-stack.peek()-1 )*h); } stack.push(i); } res=Math.max(res,area); } return res; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 "" " 单调栈 " "" class Solution public int largestRectangleArea (int [] heights) int [] tmp = new int [heights.length + 2 ]; System.arraycopy(heights, 0 , tmp, 1 , heights.length); Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(); int area = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length+2 ; i++) { while (!stack.isEmpty() && tmp[i] < tmp[stack.peek()]) { int h = tmp[stack.pop()]; area = Math.max(area, (i - stack.peek() - 1 ) * h); } stack.push(i); } return area; } }
每日一题 1227 同构字符串 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 "" " 用map存映射 若存在则判断是否一致 若不存在先判断t对应的字符是否已有对应 若有 则直接报错 因为不能两个字符映射到同一个字符 " "" class Solution public boolean isIsomorphic (String s, String t) Map<Character,Character> map=new HashMap<>(); for (int i=0 ;i<s.length();i++){ char s1=s.charAt(i); if (map.containsKey(s1)){ if (map.get(s1)==t.charAt(i)) continue ; else return false ; } else { if (map.containsValue(t.charAt(i))) return false ; map.put(s1,t.charAt(i)); } } return true ; } }
每日一题 1228 买卖股票的最佳时机 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 "" " 不考虑k次交易限制 用两个一维数组存 have:第i天有股票的最大利润 free:第i天没有股票的最大利润 状态转移公式为: free[i]=Math.max(free[i-1],have[i-1]+prices[i]); have[i]=Math.max(have[i-1],free[i-1]-prices[i]); " "" class Solution public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) int len=prices.length; if (len<1 ) return 0 ; int [] free=new int [len]; int [] have=new int [len]; free[0 ]=0 ; have[0 ]=-prices[0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<len;i++){ free[i]=Math.max(free[i-1 ],have[i-1 ]+prices[i]); have[i]=Math.max(have[i-1 ],free[i-1 ]-prices[i]); } return free[len-1 ]; } } "" " 考虑交易次数的限制 买入+卖出算一次交易次数 用二维数组存 free[i][j] 代表第i天手上没有股票 且交易了j次最大的利润 " "" class Solution public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) int len=prices.length; if (len<1 ) return 0 ; k=Math.min(k,len/2 ); int [][] free=new int [len][k+1 ]; int [][] have=new int [len][k+1 ]; free[0 ][0 ]=0 ; have[0 ][0 ]=-prices[0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<=k;i++){ free[0 ][i]=Integer.MIN_VALUE/2 ; have[0 ][i]=Integer.MIN_VALUE/2 ; } for (int i=1 ;i<len;i++){ have[i][0 ]=Math.max(free[i-1 ][0 ]-prices[i],have[i-1 ][0 ]); for (int j=1 ;j<=k;j++){ free[i][j]=Math.max(free[i-1 ][j],have[i-1 ][j-1 ]+prices[i]); have[i][j]=Math.max(have[i-1 ][j],free[i-1 ][j]-prices[i]); } } int res=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<=k;i++){ if (res<free[len-1 ][i]) res=free[len-1 ][i]; } return res; } }
每日一题 1229 按要求补齐数组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 "" " 贪心 一个数组[a1,a2,a3...an]当前能用和表示的数字区间为[1,cur_range],此时往数组内补充新数num,则此时能表示的区间为[1,cur_range]∩[num,cur_range + num] 所以若插入num=cur_range+1,覆盖的区间就为[1,cur_range+cur_range+1] 每次若已能覆盖的最大长度cur_range小于待实现的数num,并且已拥有的nums[pos]大于num,也就是需要插入值 统一插入cur_range+1这个数 不然的话 就用nums[pos]来增加覆盖的最大长度cur_range=cur_range+nums[pos] 当前能表示的最大数字为cur_range,则下一个需要达到的目标数字是cur_range + 1,而当前(未使用)的数组元素为num = nums[pos] 判断num与目标值cur_range + 1的大小关系: 1、如果num > cur_range + 1,则说明[cur_range + 1, num - 1]区间内的数字无法表示,必须补充插入新数。为了使插入的新数既能表示ach + 1,又能尽可能覆盖更多的数组(贪心的关键之处),插入的数字就是cur_range + 1,更新cur_range = cur_range + cur_range + 1 2、如果num < cur_range + 1,说明当前的目标值cur_range + 1必然可以实现(因为num >= 1),此时更新cur_range = cur_range + num " "" class Solution public int minPatches (int [] nums, int n) long cur_range=0 ; int pos=0 ; int res=0 ; while (cur_range<n){ if (pos>=nums.length||nums[pos]>cur_range+1 ){ res+=1 ; cur_range+=cur_range+1 ; } else { cur_range+=nums[pos]; pos+=1 ; } } return res; } }
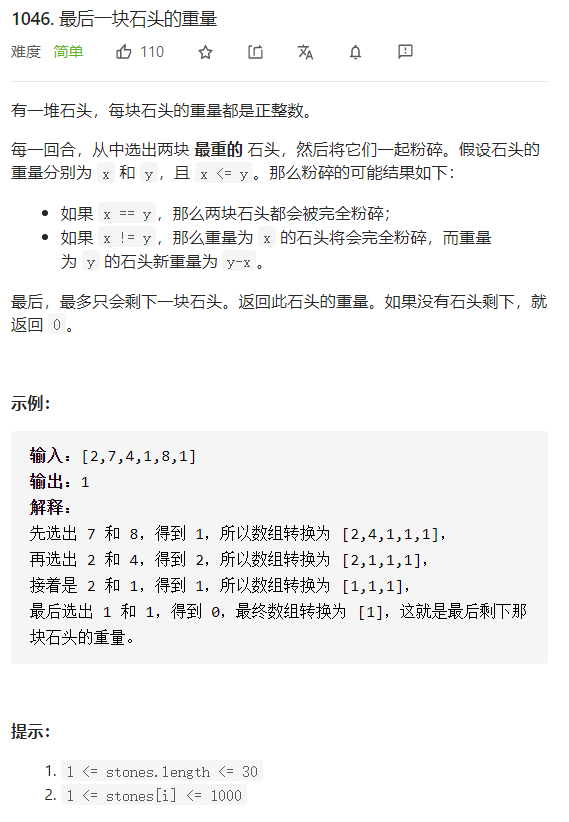
每日一题 1230 最后一块石头的重量 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "" " 用大堆来模拟过程 " "" class Solution public int lastStoneWeight (int [] stones) if (stones.length<1 ) return 0 ; PriorityQueue<Integer> queue =new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare (Integer o1, Integer o2) return o2-o1; } }); for (int i=0 ;i<stones.length;i++){ queue.offer(stones[i]); } while (queue.size()>1 ){ int m1=queue.poll(); int m2=queue.poll(); if (m1!=m2) queue.offer(m1-m2); } return queue.size()>0 ?queue.poll():0 ; } }
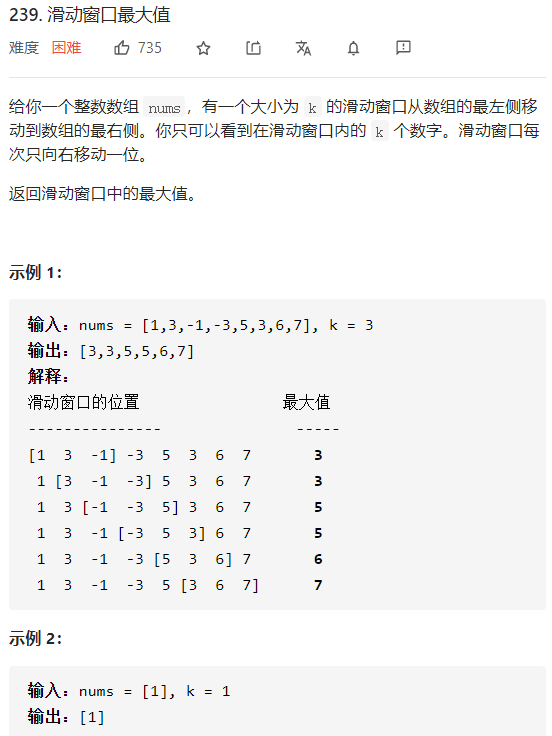
每日一题 0102 滑动窗口最大值 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 "" " 单调队列 用双端队列存一个递减队列对应的下标 " "" class Solution public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int idx=0 ; int [] res=new int [nums.length-k+1 ]; Deque<Integer> queue=new ArrayDeque<>(); for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++){ while (!queue.isEmpty()&&nums[queue.getLast()]<=nums[i]){ queue.removeLast(); } queue.addLast(i); } res[idx]=nums[queue.getFirst()]; for (int i=k;i<nums.length;i++){ while (!queue.isEmpty()&&nums[queue.getLast()]<=nums[i]){ queue.removeLast(); } queue.add(i); while (!queue.isEmpty()&&queue.peekFirst()<=i-k) queue.removeFirst(); res[++idx]=nums[queue.peekFirst()]; } return res; } }
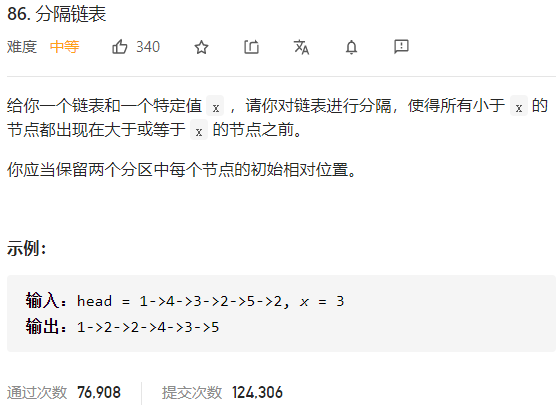
每日一题 0103 分割链表 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 "" " 维护两个链表 一个是小于x的节点 一个是大于等于x的节点 最后将小于x节点的尾结点next指向大于x的头结点即可 增加虚拟节点来统一头结点为空不为空的情况。 " "" class Solution public ListNode partition (ListNode head, int x) ListNode lhead=new ListNode(0 ); ListNode hhead=new ListNode(0 ); ListNode tmp=head; ListNode tmpl=lhead; ListNode tmph=hhead; while (tmp!=null ){ if (tmp.val<x) { tmpl.next=tmp; tmpl=tmp; } else { tmph.next=tmp; tmph=tmp; } tmp=tmp.next; } tmph.next=null ; tmpl.next=hhead.next; return lhead.next; } }
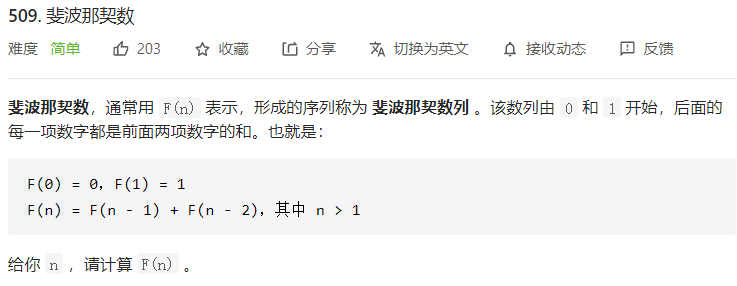
每日一题 0104 斐波那契数列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "" " 动态规划 用两个变量存状态即可 " "" class Solution public int fib (int n) int dp0=0 ,dp1=1 ,idx=2 ; if (n<2 ) return n; while (idx<=n){ int tmp=dp1; dp1=dp0+dp1; dp0=tmp; idx+=1 ; } return dp1; } }
每日一题 0105 较大分组的位置 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 一次遍历 用l指针指向重复字符的第一个位置 idx指向最后一个位置 idx-l+1即为连续字符的长度 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> largeGroupPositions(String s) { char [] arr=s.toCharArray(); List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); int l=0 ,idx=0 ; while (idx<arr.length){ while (idx+1 <arr.length&&arr[idx]==arr[idx+1 ]) { idx+=1 ; } if (idx-l+1 >=3 ){ List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<>(); tmp.add(l); tmp.add(idx); res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp)); } l=idx+1 ; idx=idx+1 ; } return res; } }
每日一题 0106 除法求值 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 "" " 图 利用除法的传递性 变量就是节点 商就是边的权值 建立图后 两个变量的商就是图中两个节点的路径乘积 " "" class Solution public double [] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double [] values, List<List<String>> queries) { Map<String,Integer> variables=new HashMap<>(); List<String> tmp_val=new ArrayList<>(2 ); int vid=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<equations.size();i++){ tmp_val=equations.get(i); if (!variables.containsKey(tmp_val.get(0 ))){ variables.put(tmp_val.get(0 ),vid++); } if (!variables.containsKey(tmp_val.get(1 ))){ variables.put(tmp_val.get(1 ),vid++); } } List<Pair>[] edges=new List[vid]; for (int i=0 ;i<vid;i++){ edges[i]=new ArrayList<Pair>(); } for (int i=0 ;i<equations.size();i++){ int ia=variables.get(equations.get(i).get(0 )),ib=variables.get(equations.get(i).get(1 )); edges[ia].add(new Pair(ib, values[i])); edges[ib].add(new Pair(ia,1 /values[i])); } int ia,ib; double [] res=new double [queries.size()]; Arrays.fill(res,-1.0 ); for (int i=0 ;i<queries.size();i++){ String sa=queries.get(i).get(0 ),sb=queries.get(i).get(1 ); if (variables.containsKey(sa)&&variables.containsKey(sb)){ ia=variables.get(sa); ib=variables.get(sb); if (ia==ib) { res[i]=1 ; continue ; } Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(ia); double [] ratios=new double [vid]; Arrays.fill(ratios,-1.0 ); ratios[ia]=1.0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()&&ratios[ib]<0 ){ int start=queue.poll(); for (Pair pair:edges[start]){ if (ratios[pair.endid]<0 ){ ratios[pair.endid]=ratios[start]*pair.val; queue.add(pair.endid); } } } res[i]=ratios[ib]; } } return res; } } class Pair int endid; double val; public Pair (int e,double v) endid=e; val=v; } }
每日一题 0107 省份数量 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 "" " 题目就是求图的连通分量个数 用dfs或者bfs 1、dfs 遍历所有城市,对于每个城市,如果该城市尚未被访问过,则从该城市开始深度优先搜索。 通过矩阵isConnected 得到与该城市直接相连的城市有哪些,这些城市和该城市属于同一个连通分量,然后对这些城市继续深度优先搜索,直到同一个连通分量的所有城市都被访问到,即可得到一个省份。 遍历完全部城市以后,即可得到连通分量的总数,即省份的总数。 " "" class Solution public int findCircleNum (int [][] isConnected) int res=0 ; int num=isConnected.length; boolean [] visited=new boolean [num]; for (int i=0 ;i<num;i++){ if (visited[i]==false ){ dfs(visited,i,isConnected); res+=1 ; } } return res; } public void dfs (boolean [] visited,int cur,int [][]isConnected) for (int j=0 ;j<visited.length;j++){ if (isConnected[cur][j]==1 &&visited[j]==false ){ visited[j]=true ; dfs(visited,j,isConnected); } } } } "" " 2、bfs 对于每个城市,如果该城市尚未被访问过,则从该城市开始广度优先搜索,直到同一个连通分量中的所有城市都被访问到,即可得到一个省份。 " "" class Solution public int findCircleNum (int [][] isConnected) int res = 0 ; int num = isConnected.length; boolean [] visited = new boolean [num]; Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>(); for (int i=0 ;i<num;i++){ if (visited[i]==false ){ queue.add(i); res+=1 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int j=queue.poll(); for (int k=0 ;k<num;k++){ if (isConnected[j][k]==1 &&visited[k]==false ){ queue.add(k); visited[k]=true ; } } } } } return res; } }
每日一题 0108 旋转数组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 "" " 1、翻转数组 向右旋转 相当于全部翻转 然后各自翻转 0~k-1 k~nums.length-1 " "" public void rotate_2 (int [] nums, int k) int n = nums.length; k %= n; reverse(nums, 0 , n - 1 ); reverse(nums, 0 , k - 1 ); reverse(nums, k, n - 1 ); } private void reverse (int [] nums, int start, int end) while (start < end) { int temp = nums[start]; nums[start++] = nums[end]; nums[end--] = temp; } } "" " 2、双重循环 每次只移动一位 " "" public void rotate_1 (int [] nums, int k) int n = nums.length; k %= n; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { int temp = nums[n - 1 ]; for (int j = n - 1 ; j > 0 ; j--) { nums[j] = nums[j - 1 ]; } nums[0 ] = temp; } }
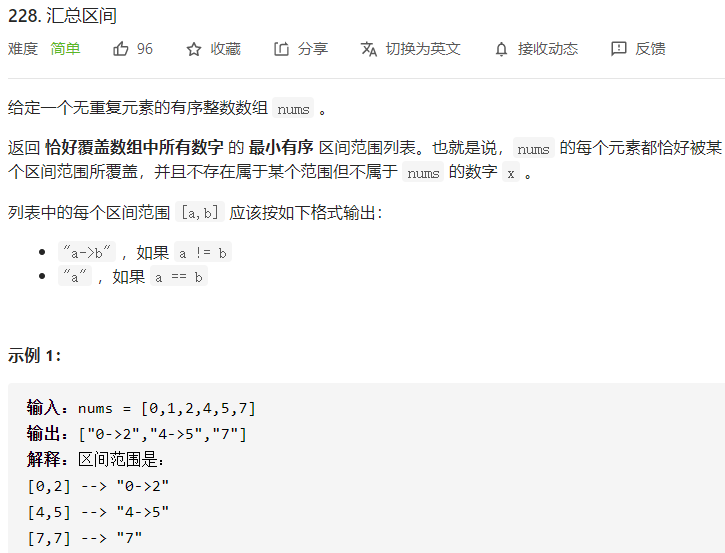
每日一题 0110 汇总区间 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 "" " 用start指向连续区间开头 每次判断nums[i]是不是区间末尾 " "" class Solution public List<String> summaryRanges (int [] nums) List<String> res=new ArrayList<>(); if (nums.length<1 ) return res; int start=nums[0 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<nums.length;i++){ if ((i<nums.length-1 &&nums[i]+1 !=nums[i+1 ])||i==nums.length-1 ){ StringBuilder tmp=new StringBuilder(); if (start!=nums[i]){ tmp.append(start).append("->" ).append(nums[i]); } else tmp.append(nums[i]); res.add(tmp.toString()); if (i<nums.length-1 ) start=nums[i+1 ]; } } return res; } }
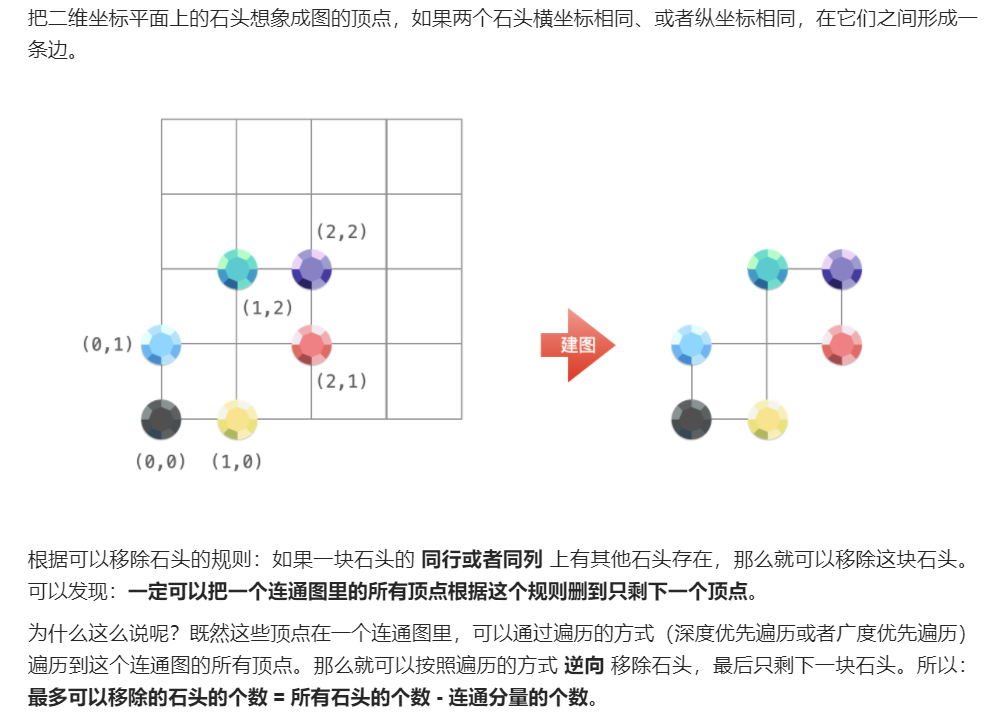
每日一题 0115 移除最多的同行或同列石头 一、问题描述
二、具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 "" " 将同行或同列的石头连接起来成图 也就是求联通分量 所有横坐标为 x 的石头和所有纵坐标为 y 的石头都属于同一个连通分量。 需要在并查集里区分「横坐标」和「纵坐标」,它们在并查集里不能相等,根据题目的提示 0 <= x_i, y_i <= 10^4,可以把其中一个坐标 映射 到另一个与 [0, 10000] 不重合的区间,可以的做法是把横坐标全部减去 10001 或者全部加上 10001 用并查集 init 初始化 find 查找节点的父节点(联通的根节点) union 合并两个节点所在的联通分量(根节点合并) 新建节点时联通分量+1,合并节点时联通分量-1 " "" class Solution public int removeStones (int [][] stones) UnionFind uf=new UnionFind(); for (int [] stone:stones){ uf.union(stone[0 ]+10001 ,stone[1 ]); } return stones.length-uf.getCount(); } } class UnionFind private Map<Integer,Integer> parent; private int count; public UnionFind () this .parent=new HashMap<>(); this .count=0 ; } public int getCount () return count; } public int find (int x) if (!parent.containsKey(x)){ parent.put(x,x); count++; } if (x!=parent.get(x)){ parent.put(x,find(parent.get(x))); } return parent.get(x); } public void union (int x,int y) int px=find(x); int py=find(y); if (px==py) return ; parent.put(px,py); count-=1 ; } }
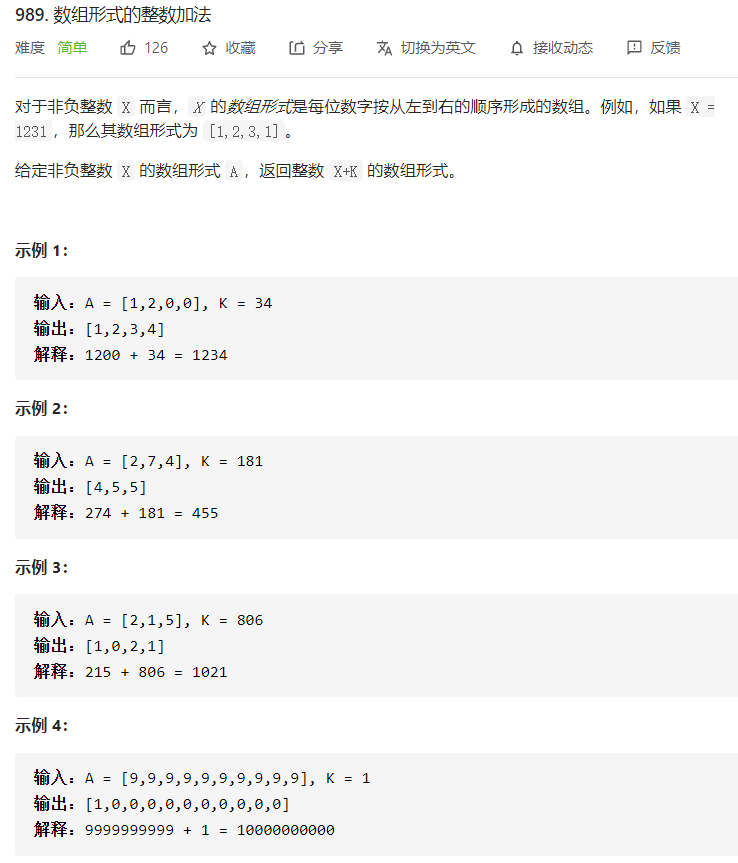
每日一题 0122 数组形式的整数加法 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 "" " 方法1 将数组的末尾以此加到数K上 去加的结果的末尾给res 也就是将进位直接体现在数K上 " "" class Solution public List<Integer> addToArrayForm (int [] A, int K) LinkedList<Integer> res=new LinkedList<>(); int tmp; int idx=A.length-1 ; int jinwei=0 ; while (K>0 ||idx>=0 ){ if (idx>=0 ){ K+=A[idx]; } res.addFirst(K%10 ); K/=10 ; idx-=1 ; } return res; } } "" " 方法2 分类讨论 无技巧 " "" class Solution public List<Integer> addToArrayForm (int [] A, int K) List<Integer> res=new LinkedList<>(); int tmp; int idx=A.length-1 ; int jinwei=0 ; while (K>0 &&idx>=0 ){ tmp=K%10 ; int tmp_add=tmp+A[idx]+jinwei; if (tmp_add<10 ){ res.add(0 ,tmp_add); jinwei=0 ; } else { res.add(0 ,tmp_add-10 ); jinwei=1 ; } idx-=1 ; K=K/10 ; } while (idx>=0 ){ int tmp_add=A[idx]+jinwei; if (tmp_add>9 ){ jinwei=1 ; res.add(0 ,tmp_add-10 ); } else { jinwei=0 ; res.add(0 ,tmp_add); } idx-=1 ; } while (K>0 ){ int tmp_add=K%10 +jinwei; if (tmp_add>9 ){ jinwei=1 ; res.add(0 ,tmp_add-10 ); } else { jinwei=0 ; res.add(0 ,tmp_add); } K/=10 ; } if (jinwei>0 ){ res.add(0 ,jinwei); } return res; } }
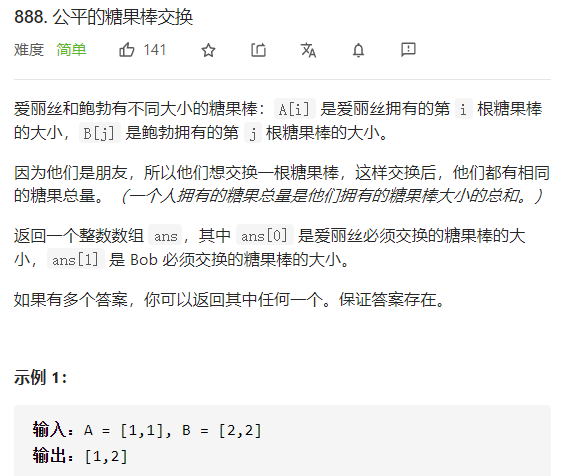
每日一题 0201 公平的糖果棒交换 一、问题描述
二、具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution public int [] fairCandySwap(int [] A, int [] B) { int sumA=Arrays.stream(A).sum(); int sumB=Arrays.stream(B).sum(); int delta=(sumA-sumB)/2 ; int [] res=new int [2 ]; Set<Integer> tmp=new HashSet<>(); for (int i=0 ;i<A.length;i++){ tmp.add(A[i]); } for (int b:B){ if (tmp.contains(b+delta)){ res[0 ]=b+delta; res[1 ]=b; return res; } } return res; } }
每日一题 0228 公平的糖果棒交换 一、问题描述
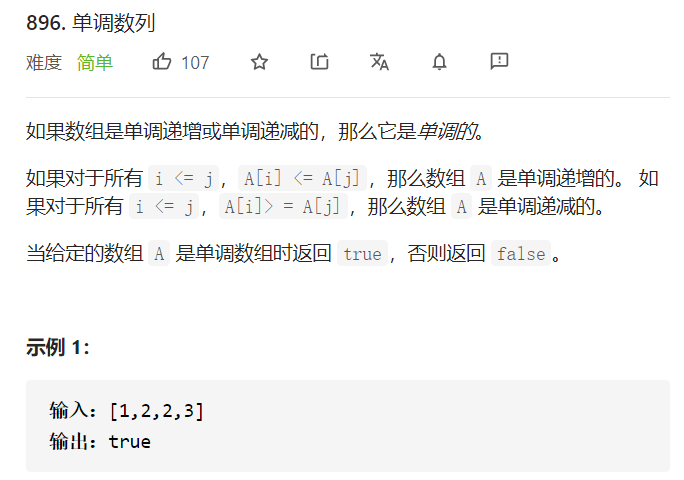
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution public boolean isMonotonic (int [] A) if (A.length<2 ) return true ; int flag=0 ; int i=1 ,len=A.length; while (i<len){ if (A[i-1 ]>A[i]) { if (flag==-1 ) return false ; flag=1 ; } if (A[i-1 ]<A[i]) { if (flag==1 ) return false ; flag=-1 ; } i+=1 ; } return true ; } }
每日一题 0301 公平的糖果棒交换 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class NumArray int [] res; public NumArray (int [] nums) if (nums.length<1 ) return ; res=new int [nums.length+1 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<nums.length;i++){ res[i+1 ]=res[i]+nums[i]; } } public int sumRange (int i, int j) return res[j+1 ]-res[i]; } }
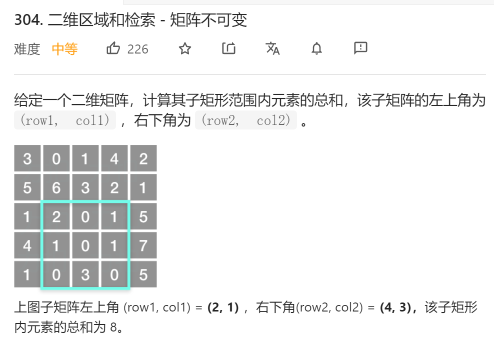
每日一题 0302 公平的糖果棒交换 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class NumMatrix public int [][] mat; public int [][] presum; public NumMatrix (int [][] matrix) this .mat=matrix; int m=matrix.length; if (m>0 ){ int n=matrix[0 ].length; presum=new int [m][n+1 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ presum[i][j+1 ]=presum[i][j]+matrix[i][j]; } } } } public int sumRegion (int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) int sum=0 ; for (int i=row1;i<=row2;i++){ sum+=presum[i][col2+1 ]-presum[i][col1]; } return sum; } }
每日一题 0303 比特位计数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution public int [] countBits(int num) { int [] dp=new int [num+1 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<=num/2 ;i++){ dp[i*2 ]=dp[i]; if (i*2 +1 <=num){ dp[i*2 +1 ]=dp[i]+1 ; } } return dp; } }
每日一题 0304 俄罗斯套娃信封问题 一、问题描述
二、具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 "" " 动态规划 首先我们将所有的信封按照 w 值第一关键字升序、h 值第二关键字降序进行排序; 随后我们就可以忽略 w 维度,求出 h 维度的最长严格递增子序列,其长度即为答案。 " "" class Solution public int maxEnvelopes (int [][] envelopes) int len=envelopes.length; if (len<2 ) return len; Arrays.sort(envelopes, new Comparator<int []>() { public int compare (int [] e1, int [] e2) if (e1[0 ] != e2[0 ]) { return e1[0 ] - e2[0 ]; } else { return e2[1 ] - e1[1 ]; } } }); int res=1 ; int [] dp=new int [len]; Arrays.fill(dp,1 ); for (int i=1 ;i<len;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<i;j++){ if (envelopes[i][1 ]>envelopes[j][1 ]){ dp[i]=Math.max(dp[j]+1 ,dp[i]); } } res=Math.max(res,dp[i]); } return res; } }
每日一题 20211227 825. 适龄的朋友 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 等式两边的0.5*x+7 和 x 都是递增 的 所以把ages排序后,用双指针 left right移动判断即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 条件3包含在了条件2里面 可以忽略 结合条件1 2 可得能通信的y的限制条件为 0.5*x+7<y<x 该等式要成立的话 x>14 那么y必>15 等式两边的0.5*x+7 和 x 都是递增的 所以把ages排序后,用双指针left right移动判断即可 " "" class Solution public int numFriendRequests (int [] ages) int num = ages.length; int res = 0 ,left = 0 , right = 0 ; Arrays.sort(ages); for (int i = 0 ; i < ages.length; i++) { if (ages[i]<15 ) continue ; while (ages[left]<=ages[i]*0.5 +7 ) left++; while (right+1 <num&&ages[right+1 ]<=ages[i]) right++; res+=right-left; } return res; } }
每日一题 20211228 560. 何为k的子数组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 "" " 由于存在负数 滑动窗口不可 方法一:固定一端 移动便利另一端 时间为N2 空间为1 方法二:前缀和+哈希简化运算 因为只要求数目,不要求 具体子数组,可以用一个map 存<前缀和为key,前缀和为k的子数组个数> 遍历求各个位置前缀和的同时,可以算得 以该数为尾端的子数组满足和为k的个数==map.get(preSum-k) 因为当前数的preSum-(preSum-k)==k 时间为N 空间为N " "" public class Solution public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) int count = 0 ; int len = nums.length; for (int left = 0 ; left < len; left++) { int sum = 0 ; for (int right = left; right < len; right++) { sum += nums[right]; if (sum == k) { count++; } } } return count; } } class Solution public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) int len = nums.length; int res = 0 ; Map<Integer,Integer> preSumMap = new HashMap<>(); preSumMap.put(0 ,1 ); int preSum = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { preSum += num; if (preSumMap.containsKey(preSum - k)) { res += preSumMap.get(preSum - k); } preSumMap.put(preSum, preSumMap.getOrDefault(preSum, 0 ) + 1 ); } return res; } }
每日一题 20211230 846. 一手顺子 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 "" " 想到用最小堆 即可完美排序加模拟找顺子的过程 从最小的数开始找满足的顺子 删除后重复找即可 " "" class Solution public boolean isNStraightHand (int [] hand, int groupSize) PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(); int len = hand.length; if (len%groupSize!=0 ) return false ; for (int j : hand) { heap.add(j); } while (!heap.isEmpty()){ int before = heap.poll(); int count = groupSize-1 ; while (count>0 ){ if (heap.contains(before+1 )){ heap.remove(before+1 ); count-=1 ; before++; }else { return false ; } } } return true ; } }
每日一题 20220102 390. 消除游戏 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/elimination-game/solution/xiao-chu-you-xi-by-leetcode-solution-ydpb/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 消除前后都是一个等差数列 直到只剩最后一个元素 观察向左删除 向右删除 等差数列第一个数的变化规律即可 " "" class Solution public int lastRemaining (int n) int al = 1 , step = 1 , nNum = n; boolean flag = true ; while (nNum>2 ){ if (flag){ al = al + step; }else { al = nNum%2 ==0 ?al:al+step; } flag = !flag; nNum = nNum>>1 ; step = step<<1 ; } return nNum==2 &&flag?al+step:al; } }
每日一题 20220103 1185. 一周中的第几天 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 "" " 求输入的日期距离 19701970 年 1212 月 3131 日的天数,可以分为三部分分别计算后求和: (1)输入年份之前的年份的天数贡献; (2)输入年份中,输入月份之前的月份的天数贡献; (3)输入月份中的天数贡献。 题目规定输入的日期一定是在 1971到 2100年之间的有效日期,即在 1971年 1 月 1 日,到 2100年 12 月 31 日之间。通过查询日历可知,1970 年 12 月 31 日是星期四,我们只需要算出输入的日期距离 1970 年 12月 31日有几天,再加上 3后对 7 求余,即可得到输入日期是一周中的第几天。 " "" class Solution public String dayOfTheWeek (int day, int month, int year) String[] week = {"Monday" , "Tuesday" , "Wednesday" , "Thursday" , "Friday" , "Saturday" , "Sunday" }; int [] monthDays = {31 , 28 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 30 }; int days = 365 * (year - 1971 ) + (year - 1969 ) / 4 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < month - 1 ; ++i) { days += monthDays[i]; } if ((year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 )) && month >= 3 ) { days += 1 ; } days += day; return week[(days + 3 ) % 7 ]; } }
每日一题 20220106 71. 简化路径 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 "" " 用栈模拟路径递进 采用双向栈 因为最后恢复字符串是要逆序退栈的 " "" class Solution public String simplifyPath (String path) Deque<String> stack = new ArrayDeque<>(); String[] paths = path.split("/" ); for (String s : paths){ if (s.equals(".." )){ if (!stack.isEmpty()){ stack.pollLast(); } }else if (s.length()>0 &&!s.equals("." )){ stack.offerLast(s); } } StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); if (stack.isEmpty()){ stringBuilder.append("/" ); }else { while (!stack.isEmpty()){ stringBuilder.append("/" ); stringBuilder.append(stack.pollFirst()); } } return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
每日一题 20220107 1614. 括号的最大嵌套深度 一、问题描述 求有效合法字符串 里面的括号嵌套深度
输入:s = “(1+(2*3)+((8)/4))+1”
输出:3
解释:数字 8 在嵌套的 3 层括号中。二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 "" " 只需要计算括号嵌套个数 不用栈 因为字符串本身有效 左括号与右括号必然匹配,所以遇到左括号加一 遇到右括号减一 求遍历中计数器最大值即可 " "" class Solution public int maxDepth (String s) char [] arrs = s.toCharArray(); int depth = 0 ; int tmpdepth = 0 ; for (char ch : arrs){ if (ch=='(' ) { tmpdepth++; depth = Math.max(depth,tmpdepth); } if (ch == ')' ) tmpdepth--; } return depth; } }
每日一题 20220108 89. 格雷编码 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gray-code/solution/ge-lei-bian-ma-by-leetcode-solution-cqi7/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "" " 方法一:格雷码第i位 相当于i向左移一位与i异或的值 方法二:格雷码为n对应的 相当于n-1的全部前面补零 + n-1的全部前面补1后翻转 2的n次方==1<<n i整体向右移一位==i>>1 " "" class Solution public List<Integer> grayCode (int n) List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); res.add(0 ); for (int i=1 ;i<(1 <<n);i++){ res.add((i>>1 )^i); } return res; } }
每日一题 20220110 306. 累加数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 "" " dfs " "" class Solution public boolean isAdditiveNumber (String num) return dfs(num, 0 , 0 ,0 ,0 ); } private boolean dfs (String num, int idx, long pre, long prepre, int count) if (idx>=num.length()){ return count>2 ; } long current = 0 ; for (int i = idx;i<num.length();i++){ int curNum = num.charAt(i)-'0' ; if (num.charAt(idx)=='0' &&i>idx){ return false ; } current = current*10 + curNum; if (count>=2 ){ long sum = pre + prepre; if (sum>current){ continue ; } if (sum<current){ return false ; } } if (dfs(num,i+1 ,current,pre,count+1 )){ return true ; } } return false ; } }
每日一题 20220112 334. 递增的三元子序列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 "" " minNum[i] 记录nums[0~i]的最小值 maxNum[i] 记录nums[i~n-1]的最大值 " "" class Solution public boolean increasingTriplet (int [] nums) int n = nums.length; int [] minNum = new int [n]; minNum[0 ] = nums[0 ]; int [] maxNum = new int [n]; maxNum[n-1 ] = nums[n-1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) { minNum[i] = Math.min(minNum[i-1 ], nums[i]); } for (int i = n-2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { maxNum[i] = Math.max(maxNum[i+1 ], nums[i]); } for (int i = 1 ; i < n-1 ; i++) { if (nums[i]>minNum[i-1 ] && nums[i]<maxNum[i+1 ]){ return true ; } } return false ; } } "" " 贪心,使前两个数尽可能小 赋初始值的时候,已经满足second > first了,现在找第三个数third (1) 如果third比second大,那就是找到了,直接返回true (2) 如果third比second小,但是比first大,那就把second的值设为third,然后继续遍历找thrid (3) 如果third比first还小,那就把first的值设为third,然后继续遍历找thrid(这样的话first会跑到second的后边,但是不要紧,因为在second的前边,老first还是满足的) " "" class Solution public boolean increasingTriplet (int [] nums) int n = nums.length; int first = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int second = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int num : nums) { if (num<=second) second = num; else if (num<=first) first = num; else return true ; } return false ; } }
每日一题 20220113 747. 至少是其他数字两倍的最大数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 需要的最大元素需要满足的条件: 至少是数组中第二大数的两倍 那我们需要记录全局第二大的数: 1、当最大数被更新时,旧的最大数即为当前第二大数 2、假如当前数小于最大数但大于第二大数时,则当前数为第二大数 " "" class Solution public int dominantIndex (int [] nums) int maxNeed = 0 ; int resIdx = 0 ; int maxNum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (nums[i]>maxNum){ maxNeed = maxNum*2 ; resIdx = i; maxNum = nums[i]; }else { if (maxNeed < nums[i]*2 ) maxNeed = nums[i]*2 ; } } return maxNum >= maxNeed ? resIdx : -1 ; } }
每日一题 20220114 373. 查找和最小的K对数字 一、问题描述
解题思路:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-k-pairs-with-smallest-sums/solution/bu-chong-guan-fang-ti-jie-you-xian-dui-l-htf8/
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 "" " 多路归并 + 优先队列(最小堆) 我们可以将 nums2 的前 k 个索引数对 (0,0),(0,1),…,(0,k−1) 加入到队列中,每次从队列中取出元素 (x,y) 时,我们只需要将 nums1的索引增加即可,这样避免了重复加入元素【不然(0,1) (1,0)都会将(1,1)加入堆中】的问题。 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int k) { PriorityQueue<int []> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->{return nums1[a[0 ]]+nums2[a[1 ]]-nums1[b[0 ]]-nums2[b[1 ]];}); int m = nums1.length; int n = nums2.length; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0 ;i<n;i++) { heap.add(new int []{0 ,i}); } int idx = 0 ; while (idx<k && !heap.isEmpty()){ int [] minCouple = heap.poll(); List<Integer> couple = new ArrayList<>(); couple.add(nums1[minCouple[0 ]]); couple.add(nums2[minCouple[1 ]]); res.add(couple); idx++; if (minCouple[0 ]+1 <m){ heap.add(new int []{minCouple[0 ]+1 , minCouple[1 ]}); } } return res; } }
每日一题 20220115 1716. 计算力扣银行的钱 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 "" " 数学推导: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 = 第一行+7*1 3 4 5 ... = 第一行+7*2 " "" class Solution public int totalMoney (int n) int mod = n%7 ; int multi7 = n/7 ; int res = ((mod+1 )*mod)/2 + mod*multi7 + (multi7-1 )*(multi7)/2 *7 + + multi7*(7 *8 /2 ); return res; } }
每日一题 20220116 382. 链表随机节点 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 "" " 1、空间换时间 用数组存节点值 random得下标 2、蓄水池算法 从链表头开始,遍历整个链表,对遍历到的第 i 个节点,随机选择区间 [0,i) 内的一个整数,如果其等于 0,则将答案置为该节点值,否则答案不变。 该算法会保证每个节点的值成为最后被返回的值的概率均为 1/n random.nextInt(idx)返回[0,idx) 注意右开 等于[0,idx-1] " "" class Solution ListNode list; Random random; public Solution (ListNode head) this .list = head; random = new Random(); } public int getRandom () int idx = 2 ; ListNode cur = list; int res = cur.val; while (cur.next!=null ){ ==0 if (random.nextInt(idx)==0 ){ res = cur.next.val; } idx++; cur = cur.next; } return res; } }
每日一题 20220117 1220.统计元音字母序列的数目 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 "" " 最开始有a,e,i,o,u四种选择 第二步根据第一步的选择有不同的发展: a->e e->a,i i->a,e,o,u o->i,u u->a 也就是第二步为a的数目=第一步为e,i,u的数目和 以此类推 " "" class Solution public int countVowelPermutation (int n) long modNum = 1000000007 ; long a = 1L , e = 1L , i = 1L , o = 1L , u = 1L ; for (int idx = 1 ;idx<n;idx++){ long aa = (e+i+u)%modNum; long ee = (a+i)%modNum; long ii = (e+o)%modNum; long oo = i; long uu = (i+o)%modNum; a = aa; e = ee; i = ii; o = oo; u = uu; } return (int )((a+e+i+o+u)%modNum); } }
每日一题 20220118 539.最小时间差 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 "" " 排序 然后将时间转化为分 返回邻近最小 或者首尾差值 " "" class Solution public int findMinDifference (List<String> timePoints) Collections.sort(timePoints); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int t0Minutes = getMinutes(timePoints.get(0 )); int preMinutes = t0Minutes; for (int i = 1 ; i < timePoints.size(); ++i) { int minutes = getMinutes(timePoints.get(i)); ans = Math.min(ans, minutes - preMinutes); preMinutes = minutes; } ans = Math.min(ans, t0Minutes + 1440 - preMinutes); return ans; } public int getMinutes (String t) String[] tmp = t.split(":" ); int hour = Integer.parseInt(tmp[0 ]); int second = Integer.parseInt(tmp[1 ]); int seconds = hour*60 + second; return seconds; } }
每日一题 20220119 219.存在重复元素 II 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 "" " 空间换时间 从小遍历 map存<数,最近出现的下标> " "" class Solution public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate (int [] nums, int k) Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0 ;i<nums.length;i++){ int num = nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(num)) { int preIdx = map.get(num); if (i - preIdx <= k) return true ; } map.put(num, i); } return false ; } } "" " 滑动窗口 维持一个k长的窗口 遍历到nums[i]时,删除nums[i-k-1]; 假如set中有nums[i] 则return true,不然就加进去 " "" class Solution public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate (int [] nums, int k) Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (i>k){ set.remove(nums[i-k-1 ]); } if (set.contains(nums[i])) return true ; set.add(nums[i]); } return false ; } }
每日一题 20220121 1345.跳跃游戏 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 "" " 当前元素下标i最小操作次数step(i)=min(step(i-1)+1, step(i+1)+1, min(step(等值)+1)); 可以想象成一个无向图 所有数为节点,当前节点直接与上一节点,下一节点 等值节点相连 权重为1 ==> 求到达最终节点的最短路径 采用dfs (队列存当前可访问节点) " "" class Solution public int minJumps (int [] arr) Map<Integer, List<Integer>> sameValueIdxs = new HashMap<>(); int len = arr.length; for (int i = len-1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { List<Integer> idxs= sameValueIdxs.getOrDefault(arr[i], new ArrayList<>()); idxs.add(i); sameValueIdxs.put(arr[i], idxs); } Deque<int []> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); queue.add(new int []{0 ,0 }); Set<Integer> visitedNodeIdxs = new HashSet<>(); visitedNodeIdxs.add(0 ); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int [] cur = queue.pollFirst(); int curIdx = cur[0 ], step = cur[1 ]; if (curIdx == len-1 ) return step; List<Integer> list = sameValueIdxs.get(arr[curIdx]); if (list!=null ){ for (Integer idx : list) { if (visitedNodeIdxs.add(idx)){ queue.addLast(new int []{idx, step+1 }); } } sameValueIdxs.remove(arr[curIdx]); } if (curIdx+1 <len && visitedNodeIdxs.add(curIdx+1 )){ queue.addLast(new int []{curIdx+1 , step+1 }); } if (curIdx>0 && visitedNodeIdxs.add(curIdx-1 )){ queue.addLast(new int []{curIdx-1 , step+1 }); } } return -1 ; } }