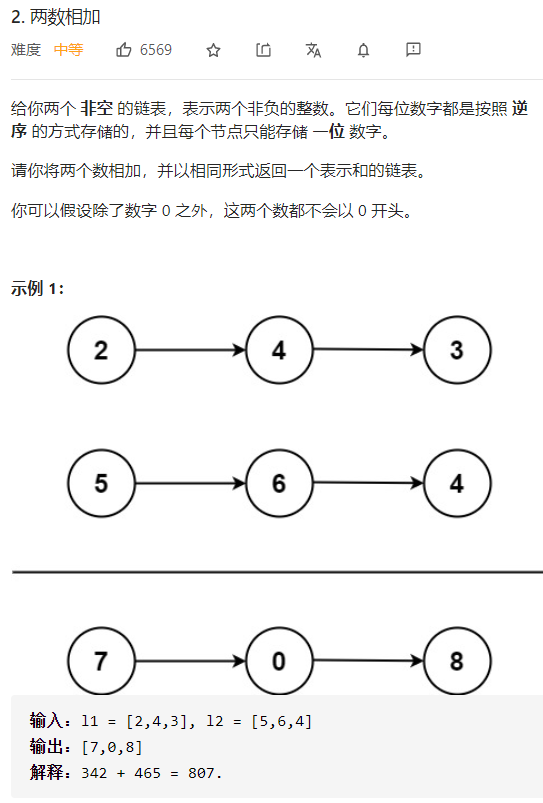
2 两数相加 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 "" " 双指针 注意进位不为空 但两个数已经遍历完的情况 " "" class Solution public ListNode addTwoNumbers (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) ListNode res = new ListNode(-1 ); ListNode cur = res; int jinwei = 0 ; while ((l1 != null && l2 != null ) || jinwei != 0 ) { int l1Val = 0 , l2Val = 0 ; if (l1 != null ) { l1Val = l1.val; l1 = l1.next; } if (l2 != null ) { l2Val = l2.val; l2 = l2.next; } int sum = (l1Val + l2Val + jinwei) % 10 ; jinwei = (l1Val + l2Val + jinwei) / 10 ; cur.next = new ListNode(sum); cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2; return res.next; } }
3 无重复字符的最长子串 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 "" " 双指针+map存数与index关系 方便查询是否出现过 " "" class Solution public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) if (s.length()<2 ) return s.length(); int left = 0 ; int res = 0 ; HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i<s.length(); i++){ if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){ left = Math.max(left, map.get(s.charAt(i))+1 ); } map.put(s.charAt(i), i); res = Math.max(res, i-left+1 ); } return res; } }
4 寻找两个正序数组的中位数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 "" " 二分 比较这两个数组的第K/2小的数字midVal1和midVal2的大小, 如果第一个数组的第K/2个数字小的话,那么说明我们要找的数字肯定不在nums1中的前K/2个数字,所以我们可以将其淘汰,将nums1的起始位置向后移动K/2个,并且此时的K也自减去K/2,调用递归。 反之,我们淘汰nums2中的前K/2个数字,并将nums2的起始位置向后移动K/2个,并且此时的K也自减去K/2,调用递归即可。 " "" class Solution public double findMedianSortedArrays (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) int m=nums1.length,n=nums2.length; int k1=(m+n+1 )/2 ,k2=(m+n+2 )/2 ; return (findk(nums1,0 ,nums2,0 ,k1)+findk(nums1,0 ,nums2,0 ,k2))/2.0 ; } public int findk (int [] nums1,int i,int [] nums2,int j,int k) if (i>=nums1.length) return nums2[j+k-1 ]; if (j>=nums2.length) return nums1[i+k-1 ]; if (k==1 ) return Math.min(nums1[i],nums2[j]); int valid1=(i+k/2 -1 <nums1.length)?nums1[i+k/2 -1 ]:Integer.MAX_VALUE; int valid2=(j+k/2 -1 <nums2.length)?nums2[j+k/2 -1 ]:Integer.MAX_VALUE; if (valid1<valid2) return findk(nums1,i+k/2 ,nums2,j,k-k/2 ); else return findk(nums1,i,nums2,j+k/2 ,k-k/2 ); } }
8 字符串转换整数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution public int myAtoi (String s) char [] str=s.toCharArray(); int i=0 ; int len=str.length; int res=0 ; int flag=1 ; while (i<len){ while (i<len&&str[i]==' ' ) i+=1 ; if (i<len&&str[i]>='a' &&str[i]<='z' ) break ; if (i<len&&(str[i]=='+' ||str[i]=='-' ) { flag=str[i]=='-' ?-1 :1 ; i+=1 ; } while (i<len&&str[i]>='0' &&str[i]<='9' ) { int digit=str[i]-'0' ; if (res>(Integer.MAX_VALUE-digit)/10 ){ if (flag<0 ) return -2147483648 ; else return 2147483647 ; } res=res*10 +str[i]-'0' ; i+=1 ; } break ; } return res*flag; } }
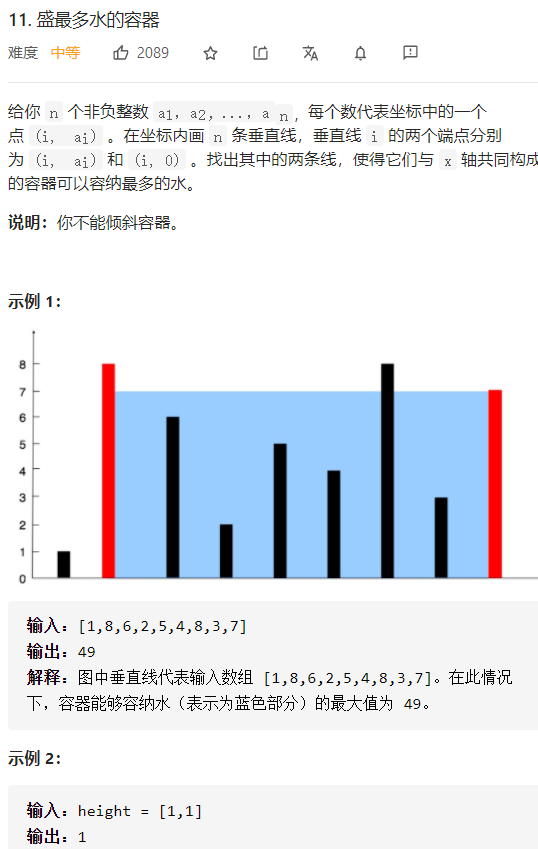
11 盛最多水的容器 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 "" " 双指针 一开始ij指向两端 随后对应高度小的那个指针向内移动、 若height[i]<height[j] i若固定不动,j向左移,则对应的水量一定小于原本的ij 若原本水量是height[i]*(j-i) j移动后为j1的水量为min(height[i],height[j1])*(j1-i)必小于原来的 因为min(height[i],height[j1])<=height[i] (j1-i)<(j-i) " "" class Solution public int maxArea (int [] height) int res=0 ; int i=0 ,j=height.length-1 ; while (i<j){ res=Math.max(res,(Math.min(height[i],height[j])*(j-i))); if (height[i]<height[j]) i++; else j--; } return res; } }
15 三数之和 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 "" " 固定一个数 相当于求数组中是否存在两个数的和等于目标值 判断两数之和 用双指针+排序: 也是固定一个数下标为second 另一个数下标为third从最右边开始移动 因为排序过 所以nums[second]+nums[third]<nums[second+1]+nums[third]<nums[second+1]+nums[third+1] 所以third只要初始化一次即可 后续直接在上一个third的基础上继续往左移 注意跳过相同的数 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res=new LinkedList<>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for (int first=0 ;first<nums.length;first++){ if (first>0 &&nums[first]==nums[first-1 ]) continue ; int target=-nums[first]; int third=nums.length-1 ; for (int second=first+1 ;second<nums.length;second++){ if (second>first+1 &&nums[second]==nums[second-1 ]) continue ; while (second<third&&nums[second]+nums[third]>target) third--; if (second==third) break ; if (nums[second]+nums[third]==target){ List<Integer> tmp=new LinkedList<>(); tmp.add(nums[first]); tmp.add(nums[second]); tmp.add(nums[third]); res.add(tmp); } } } return res; } }
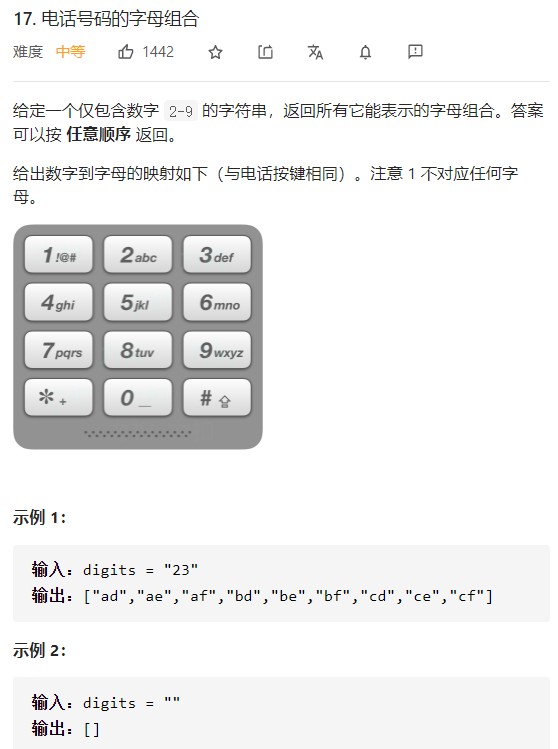
17 电话号码的字母组合 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 "" " 要全遍历 当然想到回溯 " "" class Solution Map<Character, String> phoneMap = new HashMap<Character, String>() {{ put('2' , "abc" ); put('3' , "def" ); put('4' , "ghi" ); put('5' , "jkl" ); put('6' , "mno" ); put('7' , "pqrs" ); put('8' , "tuv" ); put('9' , "wxyz" ); }}; public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) List<String> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (digits.length()<1 ) return res; int len = digits.length(); StringBuilder cur = new StringBuilder(); backtrace(res, 0 , cur, digits); return res; } private void backtrace (List<String> res,int index, StringBuilder cur, String digits) if (index == digits.length()){ res.add(cur.toString()); return ; } String curStr = phoneMap.get(digits.charAt(index)); for (int i = 0 ;i<curStr.length();i++){ cur.append(curStr.charAt(i)); backtrace(res, index+1 , cur, digits); cur.deleteCharAt(index); } } }
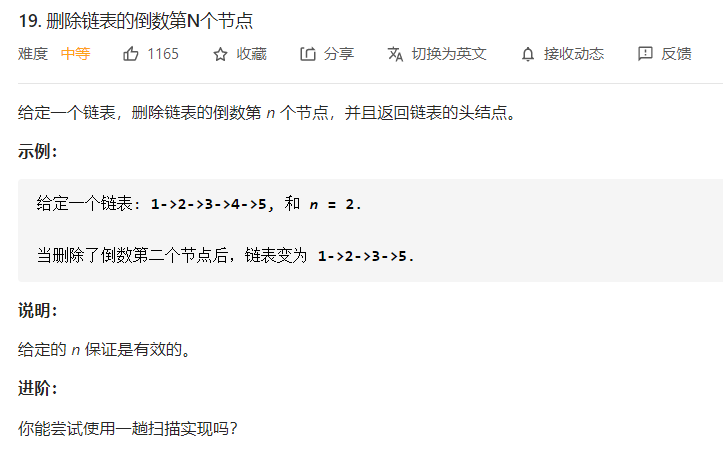
19 删除链表的倒数第N个节点 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 "" " 快慢指针 快指针先走n步 随后一起走 当快指针走到最后一个节点时,对应的慢指针指向要删除的节点的前一个节点 要注意假如要删除的是第一个指针 那直接返回head.next即可 " "" class Solution public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) ListNode fast=head; ListNode slow=head; while (n>0 ) { fast=fast.next; n-=1 ; } while (fast!=null &&fast.next!=null ){ fast=fast.next; slow=slow.next; } if (fast==null ) return slow.next; slow.next=slow.next.next; return head; } }
20 有效的括号 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 用linkedlist模仿栈 因为linkedlist是双向链表 " "" class Solution public boolean isValid (String s) LinkedList<Character> helper = new LinkedList<>(); for (int i = 0 ;i<s.length();i++){ char c = s.charAt(i); if (c == '(' || c=='[' || c=='{' ){ helper.add(c); }else { if (helper.isEmpty()) return false ; if ((c == ')' && helper.getLast()=='(' ) || (c == ']' && helper.getLast()=='[' ) || (c == '}' && helper.getLast()=='{' )){ helper.removeLast(); continue ; } return false ; } } return helper.isEmpty(); } }
21 合并两个有序链表 一、问题描述 二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 "" " 伪节点来统一空指针问题 " "" class Solution public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) ListNode pHead = new ListNode(-1 ); ListNode cur = pHead; while (l1 != null && l2 != null ){ if (l1.val < l2.val){ cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; }else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1; return pHead.next; } }
22 括号生成 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 "" " 回溯 用两个计数器记录当前左括号和右括号的个数 如果左括号数量不大于n,我们可以放一个左括号。 如果右括号数量小于左括号的数量,我们可以放一个右括号。 左括号必然在右括号之前放 所以第一个判断条件在前。 " "" class Solution public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) List<String> res=new ArrayList<>(); backtrace(res,new StringBuilder(),0 ,0 ,n); return res; } public void backtrace (List<String> res,StringBuilder cur,int open,int close,int max) if (cur.length()==max*2 ){ res.add(cur.toString()); } if (open<max){ cur.append("(" ); backtrace(res,cur,open+1 ,close,max); cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length()-1 ); } if (close<open){ cur.append(")" ); backtrace(res,cur,open,close+1 ,max); cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length()-1 ); } } } class Solution public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) List<String> res = new ArrayList<String>(); generate(res, "" , 0 , 0 , n); return res; } public void generate (List<String> res , String ans, int count1, int count2, int n) if (count1 > n || count2 > n) return ; if (count1 == n && count2 == n) res.add(ans); if (count1 >= count2){ String ans1 = new String(ans); generate(res, ans+"(" , count1+1 , count2, n); generate(res, ans1+")" , count1, count2+1 , n); } } }
23 合并k个有序链表 一、问题描述 二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 "" " k大的最小堆,k为lists的长度,每次弹出当前最小,然后把当前最小的next 若不为空 则入堆 " "" class Solution public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<ListNode>(){ @Override public int compare (ListNode o1, ListNode o2) return o1.val - o2.val; } }); int k = lists.length; if (k<1 ) return null ; ListNode pHead = new ListNode(-1 ); ListNode cur = pHead; for (ListNode list : lists){ if (list == null ) continue ; heap.add(list); } while (!heap.isEmpty()){ ListNode curMin = heap.poll(); if (curMin.next != null ){ heap.add(curMin.next); } cur.next = curMin; cur = curMin; } return pHead.next; } }
31 下一个排列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 "" " 输出全排列的下一个排列 我们需要将一个左边的「较小数」与一个右边的「较大数」交换,以能够让当前排列变大,从而得到下一个排列。 同时我们要让这个「较小数」尽量靠右,而「较大数」尽可能小。当交换完成后,「较大数」右边的数需要按照升序重新排列。这样可以在保证新排列大于原来排列的情况下,使变大的幅度尽可能小。 首先从后向前查找第一个顺序对 (i,i+1),满足 a[i]<a[i+1]。这样「较小数」即为 a[i]。此时 [i+1,n) 必然是下降序列。 如果找到了顺序对,那么在区间 [i+1,n) 中从后向前查找第一个元素 j满足a[i]<a[j]。这样「较大数」即为 a[j]。 交换 a[i]与 a[j],此时可以证明区间 [i+1,n) 必为降序。我们可以直接使用双指针反转区间 [i+1,n) 使其变为升序,而无需对该区间进行排序。 " "" class Solution public void nextPermutation (int [] nums) if (nums.length<2 ) return ; int i = nums.length - 2 ; while (i>=0 ){ if (nums[i]<nums[i+1 ]){ break ; } i--; } int j = nums.length - 1 ; if (i<0 ){ reverse(nums, 0 , nums.length-1 ); return ; } while (nums[j]<=nums[i]) j--; swap(nums, i, j); reverse(nums, i+1 , nums.length-1 ); } private void reverse (int [] nums, int left, int right) while (left<right){ swap(nums, left, right); left++; right--; } } private void swap (int [] nums, int i, int j) int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } }
32 最长有效括号 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution public int longestValidParentheses (String s) int left = 0 , right = 0 , res = 0 , startIdx = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.length();i++){ if (s.charAt(i)=='(' ) left++; else { right++; if (right==left){ res = Math.max(res, i-startIdx+1 ); } if (right>left){ startIdx = i+1 ; right = 0 ; left = 0 ; } } } left = 0 ; right = 0 ; startIdx = s.length()-1 ; for (int i=s.length()-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ if (s.charAt(i)==')' ) right++; else { left++; if (right==left){ res = Math.max(res, startIdx-i+1 ); } if (right<left){ startIdx = i-1 ; right = 0 ; left = 0 ; } } } return res; } }
33 搜索旋转排序数组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 "" " 如果中间的数小于最右边的数,则右半段是有序的, 若中间数大于最右边数,则左半段是有序的, 我们只要在有序的半段里用首尾两个数组来判断目标值是否在这一区域内,这样就可以确定保留哪半边了 " "" class Solution public int search (int [] nums, int target) int left = 0 , right = nums.length-1 ; while (left<=right){ int mid = (left+right)/2 ; if (nums[mid]==target) return mid; else if (nums[mid]<nums[right]){ if (nums[mid]<target && target<=nums[right]) left = mid+1 ; else right = mid - 1 ; }else { if (nums[mid]>target && nums[left]<=target) right = mid - 1 ; else left = mid + 1 ; } } return -1 ; } }
34 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 "" " 二分+双指针 " "" class Solution public int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length-1 ; int [] res = new int [2 ]; res[0 ] = -1 ; res[1 ] = -1 ; while (left<=right){ int mid =left + (right-left)/2 ; if (nums[mid] == target){ left = mid-1 ; right = mid+1 ; while (left>=0 &&nums[left]==target) left--; while (right<nums.length&&nums[right]==target) right++; res[0 ] = left+1 ; res[1 ] = right-1 ; return res; }else { if (nums[mid]>target) right = mid - 1 ; else left = mid + 1 ; } } return res; } }
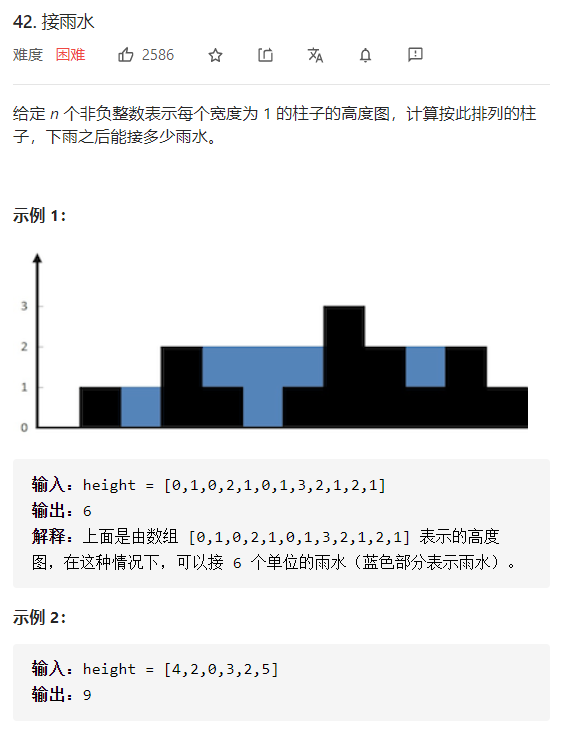
42 接雨水 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 "" " 动态规划+双指针 " "" class Solution public int trap (int [] height) int ans = 0 ; int left = 0 , right = height.length - 1 ; int leftMax = 0 , rightMax = 0 ; while (left < right) { leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, height[left]); rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, height[right]); if (leftMax < rightMax) { ans += leftMax - height[left]; ++left; } else { ans += rightMax - height[right]; --right; } } return ans; } }
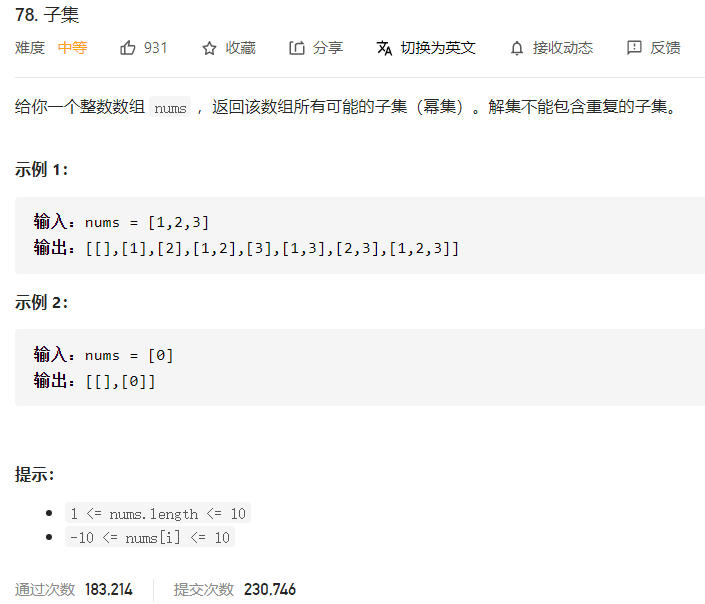
78 子集 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 "" " 从前往后遍历:遇到一个数就把所有子集加上该数组成新的子集,遍历完毕即是所有子集 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); res.add(new ArrayList<>()); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { int all = res.size(); for (int j = 0 ; j < all; j++) { List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>(res.get(j)); tmp.add(nums[i]); res.add(tmp); } } return res; } } "" " 回溯 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); res.add(new ArrayList<>()); backtrace(res,new ArrayList<>(),0 ,nums); return res; } public void backtrace (List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> cur,int idx,int [] nums) for (int i=idx;i<nums.length;i++){ cur.add(nums[i]); res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur)); backtrace(res,cur,i+1 ,nums); cur.remove(cur.size()-1 ); } } } "" " 若包含重复元素 可以用hashset 自动去除重复子集 " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int [] nums) { HashSet<ArrayList<Integer>> res=new HashSet<>(); Arrays.sort(nums); res.add(new ArrayList<>()); backtrace(res,new LinkedList<>(),0 ,nums); return new ArrayList(res); } public void backtrace (HashSet<ArrayList<Integer>> res,List<Integer> cur,int idx,int [] nums) for (int i=idx;i<nums.length;i++){ cur.add(nums[i]); res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur)); backtrace(res,cur,i+1 ,nums); cur.remove(cur.size()-1 ); } } }
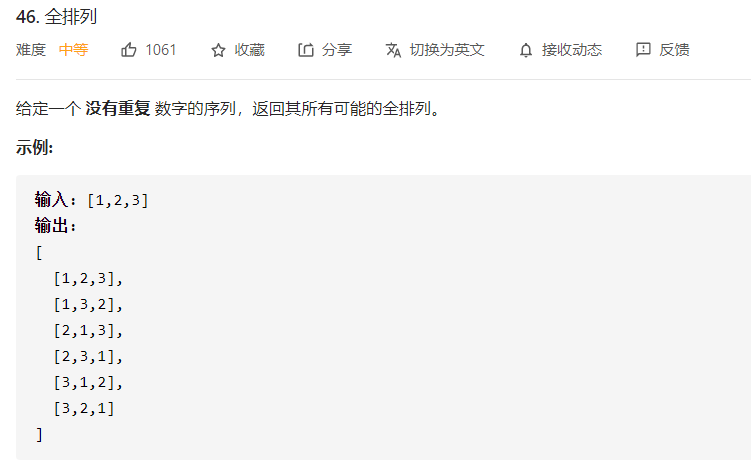
46 全排列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 "" " 回溯 用visited数组记录元素是否被访问过 " "" class Solution List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute(int [] nums) { int [] visited=new int [nums.length]; backtrace(res,new ArrayList<>(),nums,visited); return res; } public void backtrace (List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> path,int [] nums,int [] visited) if (path.size()==nums.length){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return ; } for (int i=0 ;i<nums.length;i++){ if (visited[i]==1 ) continue ; path.add(nums[i]); visited[i]=1 ; backtrace(res,path,nums,visited); path.remove(path.size()-1 ); visited[i]=0 ; } } }
49 字母异位词分组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 "" " 字母异位词每个字母出现的次数一致,于是拿字母与字母出现次数作为map 的key 比如eat ==> a1e1t1 eeaatt ==> a2e2t2 " "" class Solution public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) { Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); for (String s : strs){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); int [] count = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ;i<s.length();i++){ count[s.charAt(i)-'a' ]+=1 ; } for (int i=0 ;i<26 ;i++){ if (count[i]>0 ){ sb.append((char )('a' +i)); sb.append(count[i]); } } String key = sb.toString(); List<String> temp = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<String>()); temp.add(s); map.put(key, temp); } return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values()); } }
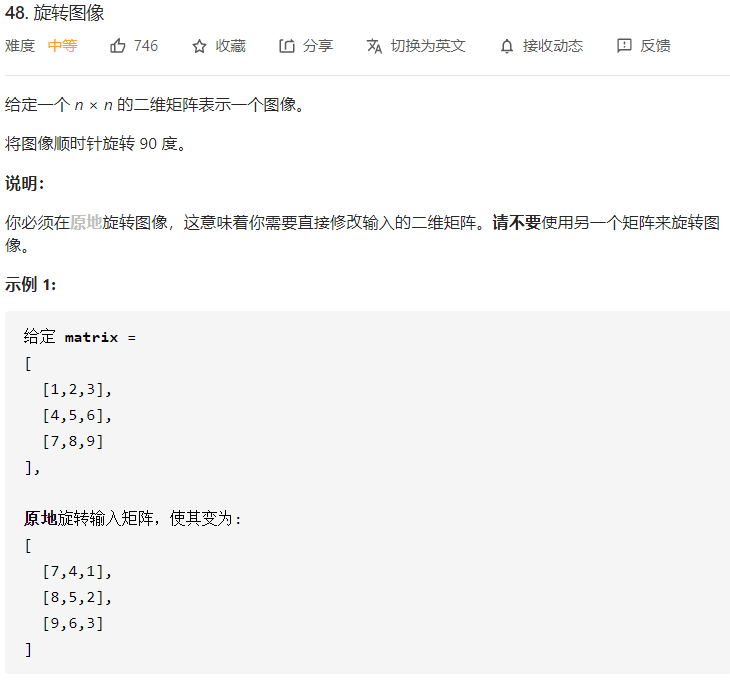
48 旋转图像 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 "" " 顺时针旋转90度=先水平翻转 再对角线翻转 " "" class Solution public void rotate (int [][] matrix) int m=matrix.length; int n=matrix[0 ].length; for (int i=0 ;i<m/2 ;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ int tmp=matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j]=matrix[m-i-1 ][j]; matrix[m-i-1 ][j]=tmp; } } for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=i+1 ;j<n;j++){ int tmp=matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j]=matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i]=tmp; } } } }
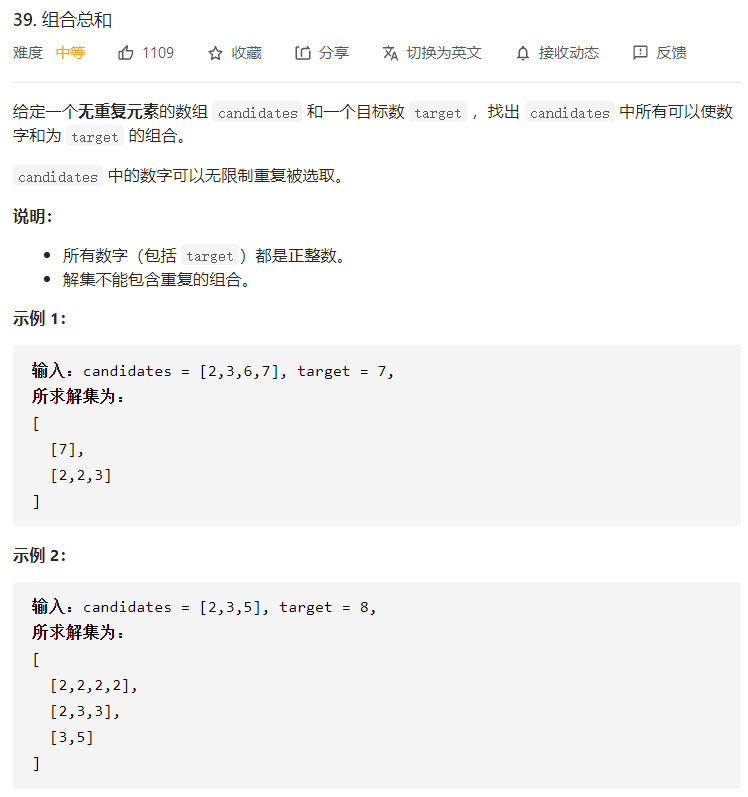
39 组合总和 即可重复选择元素进行组合 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 "" " 回溯+去重 1、正常回溯不剪枝 利用hashset去重,每次把path先排序再加入hashset " "" class Solution public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int [] candidates, int target) { HashSet<List<Integer>> res=new HashSet<>(); backtrace(res,new ArrayList<>(),0 ,candidates,target); return new ArrayList<>(res); } public void backtrace (HashSet<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> path,int cur,int [] candidates,int target) if (cur==target){ List<Integer> tmp=new ArrayList<>(path); Collections.sort(tmp); res.add(tmp); return ; } if (cur>target) return ; for (int i=0 ;i<candidates.length;i++){ path.add(candidates[i]); cur+=candidates[i]; backtrace(res,path,cur,candidates,target); cur-=candidates[i]; path.remove(path.size()-1 ); } } } "" " 2、对数组先排序 若和已大于target 后面的就不用再遍历了 因为一定更大 每次从begin开始遍历,不用倒回去 自然避免了重复 " "" class Solution List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int [] candidates, int target) { Arrays.sort(candidates); backtrace(new ArrayList<>(),0 ,candidates,target,0 ); return res; } public void backtrace (List<Integer> path,int cur,int [] candidates,int target,int begin) if (cur==target){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return ; } for (int i=begin;i<candidates.length;i++){ if (cur+candidates[i]<=target){ path.add(candidates[i]); cur+=candidates[i]; backtrace(path,cur,candidates,target,i); cur-=candidates[i]; path.remove(path.size()-1 ); } else break ; } } }
406 根据身高重建队列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 先按照身高降序 k升序进行排序 则k为该人的绝对位置 按照顺序插入结果队列中即可 " "" class Solution public int [][] reconstructQueue(int [][] people) { Arrays.sort(people, new Comparator<int []>() { @Override public int compare (int [] o1, int [] o2) if (o1[0 ]!=o2[0 ]) return o2[0 ]-o1[0 ]; else return o1[1 ]-o2[1 ]; } }); List<int []> res=new ArrayList<>(); for (int [] p:people){ res.add(p[1 ],p); } return res.toArray(new int [people.length][]); } }
238 除自身以外数组的乘积 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 遍历两次: 第一次用res数组存左乘积结果 res[i]=nums[0]*nums[1]*···*nums[i-1] 第二次用res数组存结果 即乘上右乘积的结果 res[i]=res[i]*nums[i+1]*... " "" class Solution public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) { int right=1 ; int [] res=new int [nums.length]; res[0 ]=1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<nums.length;i++){ res[i]=nums[i-1 ]*res[i-1 ]; } for (int i=nums.length-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ res[i]=res[i]*right; right=right*nums[i]; } return res; } }
208 实现Trie(前缀树) 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 "" " 前缀树是一种新的数据结构(又称字典树,前缀树,单词查找树 节点包含: private boolean is_string=false; //该节点是否是一个字符串的结尾 private Trie next[]=new Trie[26]; //该节点链接的二十六个字母指针(字母映射表) " "" public class Trie private boolean is_string=false ; private Trie next[]=new Trie[26 ]; public Trie () public void insert (String word) Trie root=this ; char w[]=word.toCharArray(); for (int i=0 ;i<w.length;++i){ if (root.next[w[i]-'a' ]==null )root.next[w[i]-'a' ]=new Trie(); root=root.next[w[i]-'a' ]; } root.is_string=true ; } public boolean search (String word) Trie root=this ; char w[]=word.toCharArray(); for (int i=0 ;i<w.length;++i){ if (root.next[w[i]-'a' ]==null )return false ; root=root.next[w[i]-'a' ]; } return root.is_string; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) Trie root=this ; char p[]=prefix.toCharArray(); for (int i=0 ;i<p.length;++i){ if (root.next[p[i]-'a' ]==null )return false ; root=root.next[p[i]-'a' ]; } return true ; } }
56 合并区间 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 "" " 先把各区间按照开始排序 假如两个区间有重叠,则取最远的end作为新数组的end即可 假如没有重叠,则前面的start end构成一个区间,新的区间的start end由后面区间构成 " "" class Solution public static int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0 ])); List<int []> res = new ArrayList<>(); int start = intervals[0 ][0 ]; int end = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ;i<intervals.length;i++){ if (intervals[i][0 ]>end){ res.add(new int []{start, end}); start = intervals[i][0 ]; } end = Math.max(end,intervals[i][1 ]); } res.add(new int []{start,end}); return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][2 ]); } }
62 不同路径 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 "" " 动态规划f(i,j)=f(i−1,j)+f(i,j−1) 当i=0或j=0的时候,只有一条路径 " "" class Solution public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ if (i==0 ||j==0 ){ dp[i][j] = 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j] + dp[i][j-1 ]; } } } return dp[m-1 ][n-1 ]; } }
64 最小路径和 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 "" " 动态规划 不过要注意初始化边界的时候: dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]+grid[i][0]; dp[0][j]=dp[0][j-1]+grid[0][j]; 是累加的不是直接=grid[0][j] " "" class Solution public int minPathSum (int [][] grid) int [][] dp=new int [grid.length][grid[0 ].length]; dp[0 ][0 ]=grid[0 ][0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<grid.length;i++){ dp[i][0 ]=dp[i-1 ][0 ]+grid[i][0 ]; } for (int j=1 ;j<grid[0 ].length;j++){ dp[0 ][j]=dp[0 ][j-1 ]+grid[0 ][j]; } for (int i=1 ;i<grid.length;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<grid[0 ].length;j++){ dp[i][j]=Math.min(dp[i-1 ][j],dp[i][j-1 ])+grid[i][j]; } } return dp[grid.length-1 ][grid[0 ].length-1 ]; } }
75 最小路径和 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "" " 三路快排 " "" class Solution public void sortColors (int [] nums) int left = 0 ; int right = nums.length-1 ; while (left<=right&&nums[left]==0 ) left++; while (right>=left&&nums[right]==2 ) right--; for (int idx =left;idx<=right;idx++){ while (idx<=right && nums[idx] == 2 ){ swap(nums, idx, right); right--; } if (nums[idx]==0 ){ swap(nums, idx ,left); left++; } } } private void swap (int [] nums, int i ,int j) int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; } }
148 排序列表 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 "" " 时间复杂度nlogn 那只能堆排序 归并排序 快排(最差n2) 常数级复杂度 那就只能归并排序 自顶向下的归并排序一般用递归 空间复杂度为n 所以要用自底向上的归并排序方法: 1、首先求得链表的长度length,然后将链表拆分成子链表进行合并。 2、用subLength 表示每次需要排序的子链表的长度,初始时subLength=1。 每次将链表拆分成若干个长度为subLength 的子链表(最后一个子链表的长度可以小于subLength),按照每两个子链表一组进行合并,合并后即可得到若干个长度为subLength×2 的有序子链表(最后一个子链表的长度可以小于2subLength×2)。 3、将subLength 的值加倍,重复第 2 步,对更长的有序子链表进行合并操作,直到有序子链表的长度大于或等于length,整个链表排序完毕。 " "" class Solution public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) if (head == null ) { return head; } int length = 0 ; ListNode node = head; while (node != null ) { length++; node = node.next; } ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0 , head); for (int subLength = 1 ; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1 ) { ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next; while (curr != null ) { ListNode head1 = curr; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr.next != null ; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode head2 = curr.next; curr.next = null ; curr = head2; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null ; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode next = null ; if (curr != null ) { next = curr.next; curr.next = null ; } ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2); prev.next = merged; while (prev.next != null ) { prev = prev.next; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead.next; } public ListNode merge (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0 ); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null ) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null ) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null ) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } } "" " 自顶向下的归并 利用快慢指针得到中间节点 一个走两步 一个走一步 " "" class Solution public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) if (head==null || head.next==null ) return head; ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next; while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null ){ slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } ListNode head1 = slow.next; slow.next = null ; return merge(sortList(head),sortList(head1)); } public ListNode merge (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0 ); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null ) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null ) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null ) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }
287 寻找重复数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 "" " Floyd算法 龟兔赛跑 线性的时间复杂度 常数级的空间复杂度 一个fast指针每次走两步,一个slow指针每次走一步 终会在不是起点的地方相遇 相遇后slow回到起点 两个一起每次走一步 最终相与的点就是环入口 " "" class Solution public int findDuplicate (int [] nums) int slow=0 ,fast=0 ; while (true ){ fast=nums[nums[fast]]; slow=nums[slow]; if (fast==slow){ slow=0 ; while (slow!=fast){ slow=nums[slow]; fast=nums[fast]; } return slow; } } } }
200 岛屿数量 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 "" " 相当于求连通区域个数 思路:遍历岛这个二维数组,如果当前数为1,则进入感染函数并将岛个数+1 感染函数:其实就是一个递归标注的过程,它会将所有相连的1都标注成2。为什么要标注?这样就避免了遍历过程中的重复计数的情况,一个岛所有的1都变成了2后,遍历的时候就不会重复遍历了 " "" class Solution public int numIslands (char [][] grid) int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < grid.length; i++) { for (int i1 = 0 ; i1 < grid[0 ].length; i1++) { if (grid[i][i1]=='1' ){ paint(grid,i,i1); res+=1 ; } } } return res; } private void paint (char [][] grid, int i,int j) if (i<0 ||j<0 ||i>grid.length-1 ||j>grid[0 ].length-1 ||grid[i][j]=='2' ||grid[i][j]=='0' ){ return ; } grid[i][j] = '2' ; paint(grid,i+1 ,j); paint(grid,i-1 ,j); paint(grid,i,j+1 ); paint(grid,i,j-1 ); } }
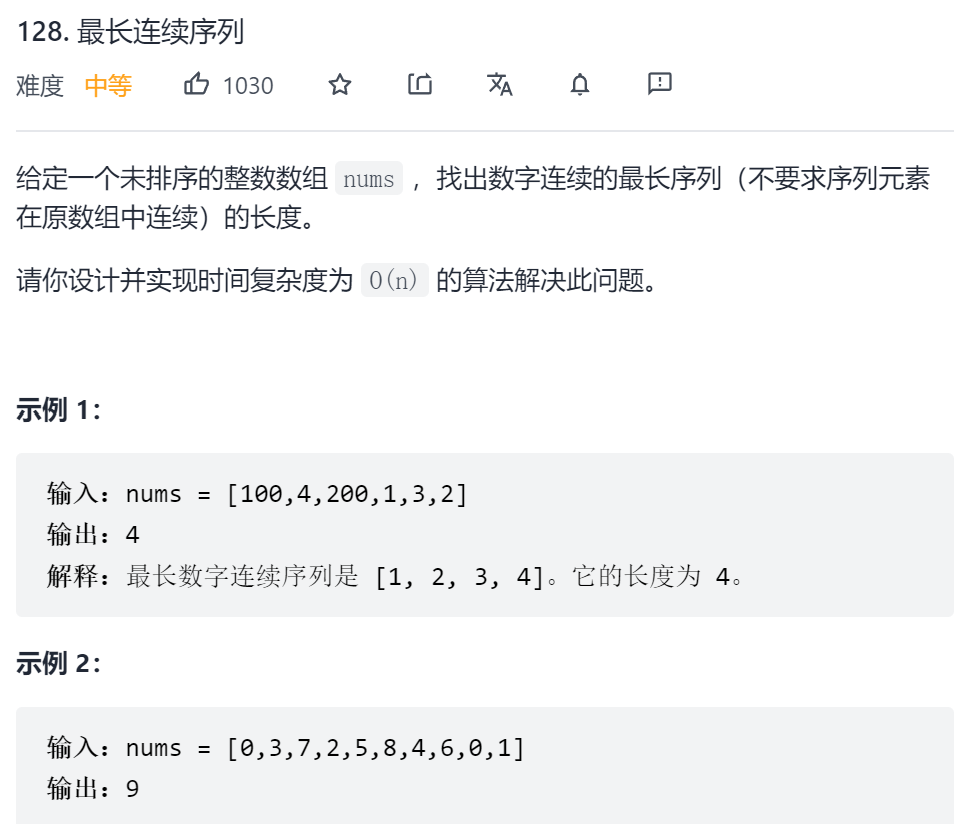
128 最长连续序列 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 "" " 暴力方法是以每个元素为起点开始向右探寻 复杂度为n2 发现会有很多重复操作, 于是 只搜索每个序列的开头x==集合中没有x-1 " "" class Solution public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); int maxLen = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { set.add(num); } for (int num : nums) { int cur = num; int curLen = 1 ; if (!set.contains(cur-1 )){ while (set.contains(cur+1 )){ cur++; curLen++; } } maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, curLen); } return maxLen; } }
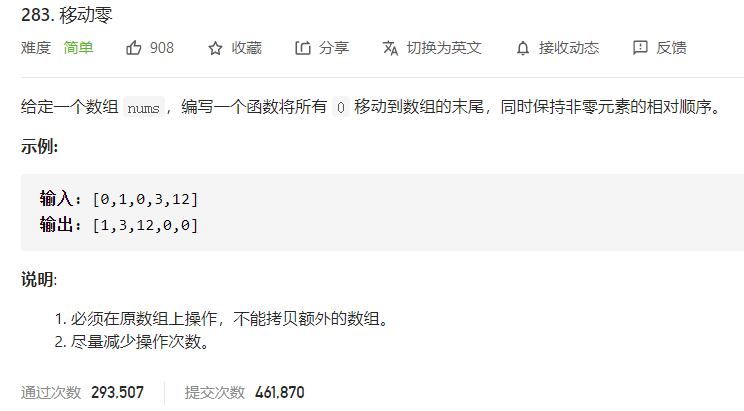
283 寻找重复数 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 "" " 1、双指针 i指向第一个零 j指向为整理的第一个非零 交换即可 " "" class Solution public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) int i=0 ,j=0 ; while (i<nums.length){ while (i<nums.length&&nums[i]!=0 ) i++; while (j<nums.length&&nums[j]==0 ) j++; if (j==nums.length||i==nums.length) return ; if (i<j){ int temp=nums[j]; nums[j]=nums[i]; nums[i]=temp; } j++; } } } "" " 2、双指针 更好 因为末尾都是零 只需要把非零的全部移到前面即可(直接覆盖) 后面的用零覆盖 " "" class Solution public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) int j = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (nums[i] != 0 ) { nums[j++] = nums[i]; } } while (j<nums.length){ nums[j++]=0 ; } } }
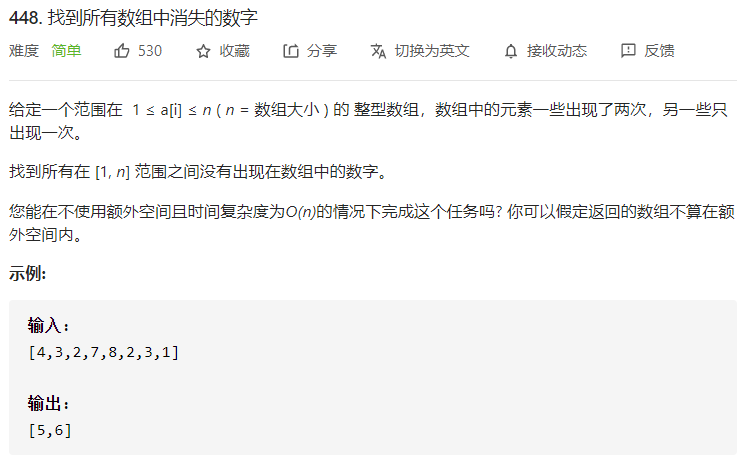
581 找到所有数组中消失的数字 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 "" " 利用数的范围都在1~n 将nums[nums[i]-1]转负数 nums[i]仍为正数的 那i+1就是没出现的 注意下标从0开始 " "" class Solution public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers (int [] nums) List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>(); int len=nums.length; for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ int tmp=Math.abs(nums[i])-1 ; if (nums[tmp]>0 ) nums[tmp]=-nums[tmp]; } for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ if (nums[i]>0 ) res.add(i+1 ); } return res; } }
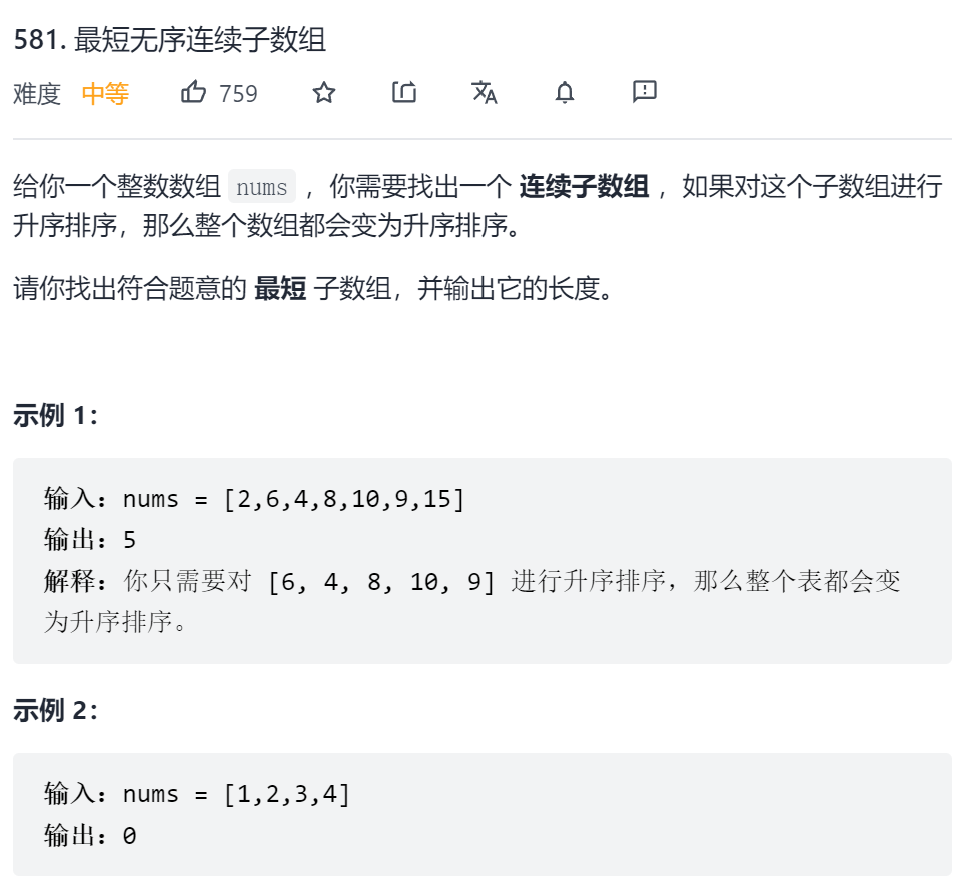
581 最长无序连续子数组 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 "" " 所给的数组可以分为三段: A B C 其中 A C都有序 且A中所有数都小于B C中的最小数 C中的所有数都大于A B中的最大数 目的就是找到最短的B 即最长的A 与 C 将B的两端用left 和right标记 left下标左边的所有数都小于右边的最小数 right下标右边的所有数都大于左边的最大数 于是要遍历 left==从右往左遍历 最靠左边的 不满足 小于右边最小数的下标 right==从左往右遍历 最靠右边的 不满足 大于左边最大数的下标 " "" class Solution public int findUnsortedSubarray (int [] nums) int len = nums.length; int minNum = nums[len-1 ]; int maxNum = nums[0 ]; int left=-1 ,right=-1 ; for (int i = len-2 ; i >=0 ; i--) { if (nums[i]<=minNum){ minNum = nums[i]; }else { left = i; } } for (int i = 1 ; i < len ; i++) { if (nums[i]>=maxNum){ maxNum = nums[i]; }else { right = i; } } return left==-1 ?0 :right-left+1 ; } }
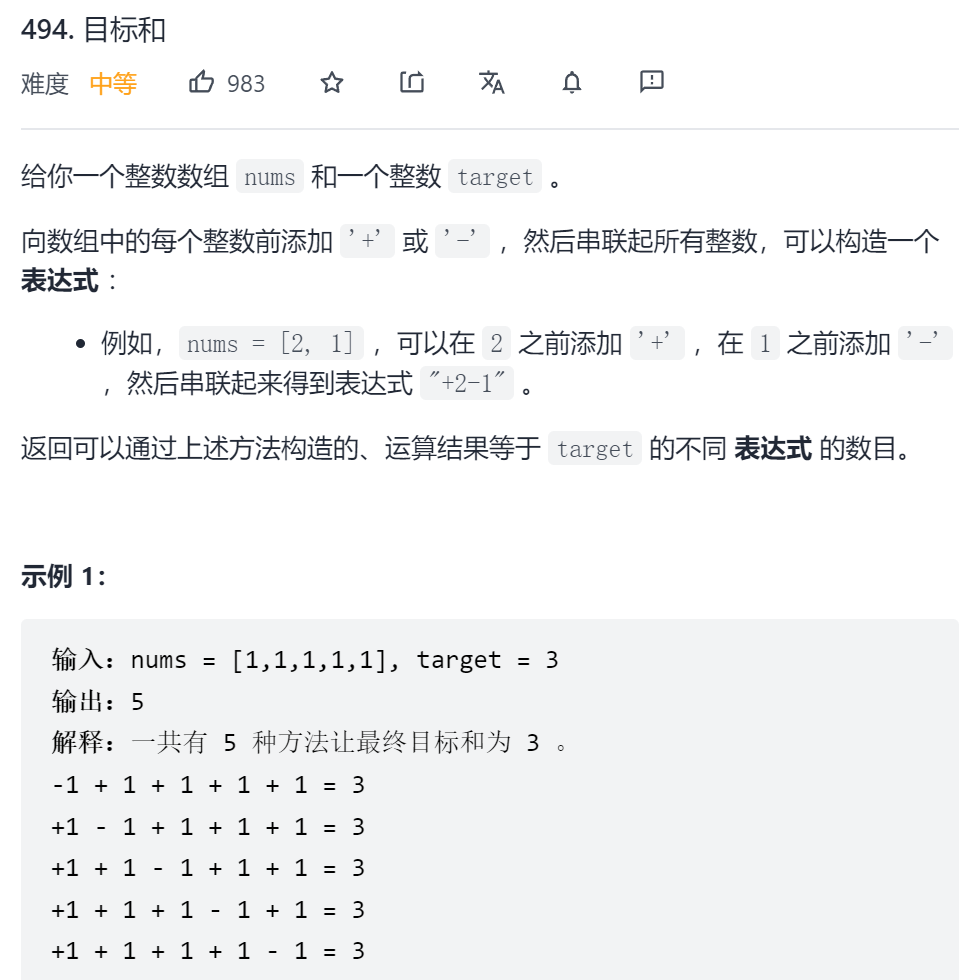
494 目标和 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/target-sum/solution/mu-biao-he-by-leetcode-solution-o0cp/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 "" " 1、回溯 每位数字有正负两种选择 时间复杂度为2的n次方 " "" class Solution int res = 0 ; public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) backtrace(nums,0 ,0 ,target); return res; } private void backtrace (int [] nums, int idx, int tmpSum, int target) if (idx==nums.length){ if (tmpSum==target){ res+=1 ; } return ; } backtrace(nums,idx+1 ,tmpSum+nums[idx],target); backtrace(nums,idx+1 ,tmpSum-nums[idx],target); } } "" " 整个符合target要求的集合可以分为两个集合P1(+) P2(-) P1(+) + P2(-) = target P1(+) + P1(+) + P2(-) +P2(+) = target + P1(+) +P2(+) 2P1(+) = target + 所有元素的集合 就将原问题转化为 求集合中有多少个子集和满足条件的问题 可以用动态规划 dp[i][j]=前i个元素中包含子集和等于j的个数 假如第i个元素nums[i]>j 那么 dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]因为肯定不会选nums[i] 假如小于等于j,那么dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-nums[i]] 边界条件:dp[i][0]=1(全不选) dp[0][j]=0(j>0) " "" class Solution public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) int sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { sum += num; } int diff = sum - target; if (diff < 0 || diff % 2 != 0 ) { return 0 ; } int n = nums.length, neg = diff / 2 ; int [][] dp = new int [n + 1 ][neg + 1 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int num = nums[i - 1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j <= neg; j++) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j]; if (j >= num) { dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1 ][j - num]; } } } return dp[n][neg]; } } "" " 一维数组 " "" class Solution public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) int sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums) { sum += num; } int diff = sum - target; if (diff < 0 || diff % 2 != 0 ) { return 0 ; } int neg = diff / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [neg + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int num : nums) { for (int j = neg; j >= num; j--) { dp[j] += dp[j - num]; } } return dp[neg]; } }
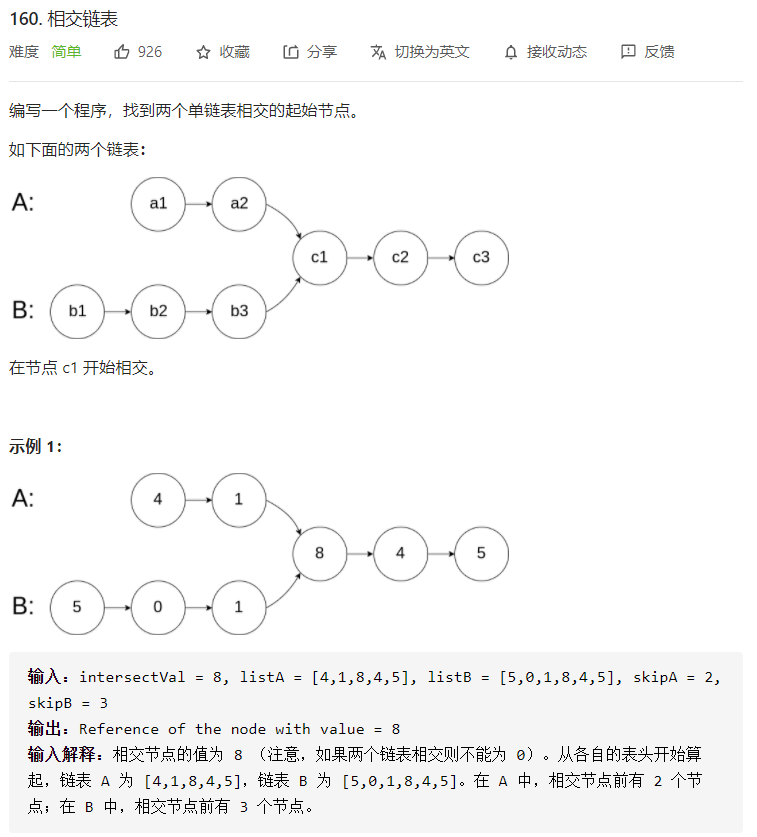
160 相交链表 一、问题描述
二、具体代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 "" " 1、神之方法:定义两个指针, 第一轮让两个到达末尾的节点指向另一个链表的头部, 最后如果相遇则为交点(在第一轮移动中恰好抹除了长度差) 两个指针等于移动了相同的距离, 有交点就返回, 无交点就是各走了两条指针的长度 时间复杂度m(a的长度减去公共的)+n(b的长度减去公共的)+p(公共的) " "" public class Solution public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) ListNode pa=headA,pb=headB; if (pa==null ||pb==null ) return null ; while (pa!=pb){ pa=pa==null ?headB:pa.next; pb=pb==null ?headA:pb.next; } return pa; } } "" " 2、分别计算两者的长度len_a,len_b 然后长的先走abs(len_a-len_b)步 随后a,b两者一起走,相交点就是交点 时间复杂度max(a+b)+abs(a-b)+min(a,b)-p " "" public class Solution public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) ListNode pa=headA; ListNode pb=headB; int len_A=0 ; int len_B=0 ; while (pa!=null ){ pa=pa.next; len_A+=1 ; } while (pb!=null ){ pb=pb.next; len_B+=1 ; } pa=headA; pb=headB; if (len_A>=len_B){ int count=len_A-len_B; while (count>0 ){ pa=pa.next; count-=1 ; } while (pa!=pb){ pa=pa.next; pb=pb.next; } } else { int count=len_B-len_A; while (count>0 ){ pb=pb.next; count-=1 ; } while (pa!=pb){ pa=pa.next; pb=pb.next; } } return pa; } }
title: N Queen
N皇后问题 github 51题 问题描述
使用回溯 算法
参考了labuladong大佬的算法框架
框架链接
##具体代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 class Solution List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) { char [][] board = new char [n][n]; for (char [] c : board) { Arrays.fill(c, '.' ); } backtrack(board, 0 ); return res; } public void backtrack (char [][] board, int row) if (row == board.length) { res.add(charToList(board)); return ; } int n = board[row].length; for (int col = 0 ; col < n; col++) { if (!isValid(board, row, col)) { continue ; } board[row][col] = 'Q' ; backtrack(board, row + 1 ); board[row][col] = '.' ; } } public boolean isValid (char [][] board, int row, int col) int n = board.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (board[i][col] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col + 1 ; i >=0 && j < n; i--, j++) { if (board[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i = row - 1 , j = col - 1 ; i >= 0 && j >= 0 ; i--, j--) { if (board[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } return true ; } public List charToList (char [][] board) List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (char [] c : board) { list.add(String.copyValueOf(c)); } return list; } }
title: 面试题
最长回文子串 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 "" " 以中间为拓展起点 双指针向两端遍历 注意中心1个或2个 " "" class Solution public String longestPalindrome (String s) int len=s.length(); int res=0 ; String temp="" ; for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<=1 ;j++){ int l=i,r=i+j; while (l>=0 &&r<len&&s.charAt(l)==s.charAt(r)) {l--;r++;} if (res<r-l-1 ){ res=r-l-1 ; temp=s.substring(l+1 ,r); } } } return temp; } }
合并链表 归并排序
1、利用快慢指针 找到链表中央节点
2、将链表一分为二进行分别排序
3、合并两个有序链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public ListNode sortInList (ListNode head) if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } return mergeSort(head); } public ListNode mergeSort (ListNode head) if (head.next == null ) { return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head, pre = null ; while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) { pre = slow; slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } pre.next = null ; ListNode left = mergeSort(head); ListNode right = mergeSort(slow); return merge(left, right); } public ListNode merge (ListNode left, ListNode right) ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1 ); ListNode cur = dummy; while (left != null && right != null ) { if (left.val < right.val) { cur.next = left; left = left.next; } else { cur.next = right; right = right.next; } cur = cur.next; } if (left != null ) { cur.next = left; } if (right != null ) { cur.next = right; } return dummy.next; }
前缀树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class Trie private boolean is_string=false ; private Trie next[]=new Trie[26 ]; public Trie () public void insert (String word) Trie root=this ; char w[]=word.toCharArray(); for (int i=0 ;i<w.length;++i){ if (root.next[w[i]-'a' ]==null )root.next[w[i]-'a' ]=new Trie(); root=root.next[w[i]-'a' ]; } root.is_string=true ; } public boolean search (String word) Trie root=this ; char w[]=word.toCharArray(); for (int i=0 ;i<w.length;++i){ if (root.next[w[i]-'a' ]==null )return false ; root=root.next[w[i]-'a' ]; } return root.is_string; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) Trie root=this ; char p[]=prefix.toCharArray(); for (int i=0 ;i<p.length;++i){ if (root.next[p[i]-'a' ]==null )return false ; root=root.next[p[i]-'a' ]; } return true ; } }
最大公约数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int max = a > b ? a : b; int min = a < b ? a : b; if (max % min == 0 ) return min; return gcd(max % min, min); int max = a > b ? a : b; int min = a < b ? a : b; if (max % min == 0 ) return min; return gcd(max - min, min); while (a != b){ if (a > b) a -= b; else b -= a; } return a;
立方根 牛顿迭代法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 "" " 二分法 " "" double fun (double x) if (x == 0 ) return 0 ; double low = 0 ; double top = x; if (x < 0 ) { low = x; top = 0 ; } while (low<top) { double mid = (low + top) / 2 ; double tmp = mid*mid*mid; if (tmp > x) { top = mid; } else if (tmp < x) { low = mid; } else { return mid; } } } import java.util.*;public class Main public static void main (String[] args) Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); double n = sc.nextDouble(); double m = get(n); System.out.println(String.format("%.1f" ,m)); } public static double get (double n) double a, b; a = n; if (n == 0 ){ return 0 ; } b = (2 * a + n / a / a) / 3 ; while (Math.abs(b - a) > 0.000001 ){ a = b; b = (2 * a + n / a / a) / 3 ; } return b; } }